Growth, development, and gene expression in a persistent Streptococcus gordonii biofilm
- PMID: 12874358
- PMCID: PMC166047
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.8.4759-4766.2003
Growth, development, and gene expression in a persistent Streptococcus gordonii biofilm
Abstract
A model for the protracted (30-day) colonization of smooth surfaces by Streptococcus gordonii that incorporates the nutrient flux that occurs in the oral cavity was developed. This model was used to characterize the biphasic expansion of the adherent bacterial population, which corresponded with the emergence of higher-order architectures characteristic of biofilms. Biofilm formation by S. gordonii was observed to be influenced by the presence of simple sugars including sucrose, glucose, and fructose. Real-time PCR was used to quantify changes in expression of S. gordonii genes known or thought to be involved in biofilm formation. Morphological changes were accompanied by a significant shift in gene expression patterns. The majority of S. gordonii genes examined were observed to be downregulated in the biofilm phase. Genes found to be upregulated in the biofilm state were observed to encode products related to environmental sensing and signaling.
Figures

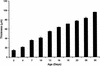
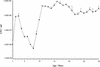

Similar articles
-
Involvement of an inducible fructose phosphotransferase operon in Streptococcus gordonii biofilm formation.J Bacteriol. 2003 Nov;185(21):6241-54. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.21.6241-6254.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 14563858 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of the adc operon and manganese homeostasis in Streptococcus gordonii biofilm formation.J Bacteriol. 2003 May;185(9):2887-900. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.9.2887-2900.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 12700268 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of green fluorescent protein in Streptococcus gordonii DL1 and its use as a species-specific marker in coadhesion with Streptococcus oralis 34 in saliva-conditioned biofilms in vitro.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000 Sep;66(9):4074-83. doi: 10.1128/AEM.66.9.4074-4083.2000. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10966431 Free PMC article.
-
Critical roles of arginine in growth and biofilm development by Streptococcus gordonii.Mol Microbiol. 2015 Jul;97(2):281-300. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13023. Epub 2015 May 20. Mol Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25855127
-
Streptococcus gordonii biofilm formation: identification of genes that code for biofilm phenotypes.J Bacteriol. 2000 Mar;182(5):1374-82. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.5.1374-1382.2000. J Bacteriol. 2000. PMID: 10671461 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
LuxS-based signaling affects Streptococcus mutans biofilm formation.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 May;71(5):2372-80. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.5.2372-2380.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15870324 Free PMC article.
-
Manganese affects Streptococcus mutans virulence gene expression.Caries Res. 2007;41(6):503-11. doi: 10.1159/000110883. Epub 2007 Nov 8. Caries Res. 2007. PMID: 17992013 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Streptococcus sanguinis genes required for biofilm formation and examination of their role in endocarditis virulence.Infect Immun. 2008 Jun;76(6):2551-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00338-08. Epub 2008 Apr 7. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18390999 Free PMC article.
-
Type IV pili and the CcpA protein are needed for maximal biofilm formation by the gram-positive anaerobic pathogen Clostridium perfringens.Infect Immun. 2008 Nov;76(11):4944-51. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00692-08. Epub 2008 Sep 2. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18765726 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological Observation and Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of Clostridium perfringens Biofilm and Planktonic Cells.Curr Microbiol. 2018 Sep;75(9):1182-1189. doi: 10.1007/s00284-018-1507-z. Epub 2018 May 11. Curr Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29752494
References
-
- Burne, R. A., Y. Y. Chen, and J. E. Penders. 1997. Analysis of gene expression in Streptococcus mutans in biofilms in vitro. Adv. Dent. Res. 11:100-109. - PubMed
-
- Chatenay-Rivauday, C., I. Yamodo, M. A. Sciotti, N. Troffer-Charlier, J. P. Klein, and J. Ogier. 2000. TNF-α release by monocytic THP-1 cells through cross-linking of the extended V-region of the oral streptococcal protein I/II. J. Leukoc. Biol. 67:81-89. - PubMed
-
- Clemans, D. L., P. E. Kolenbrander, D. V. Debabov, Q. Zhang, R. D. Lunsford, H. Sakone, C. J. Whittaker, M. P. Heaton, and F. C. Neuhaus. 1999. Insertional inactivation of genes responsible for the d-alanylation of lipoteichoic acid in Streptococcus gordonii DL1 (Challis) affects intrageneric coaggregations. Infect. Immun. 67:2464-2474. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

