The fibrinolytic system in dissemination and matrix protein deposition during a mycobacterium infection
- PMID: 12875972
- PMCID: PMC1868210
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63680-2
The fibrinolytic system in dissemination and matrix protein deposition during a mycobacterium infection
Abstract
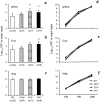
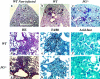
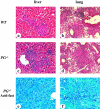
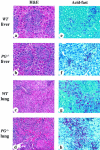
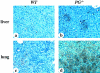
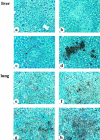
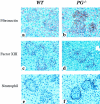
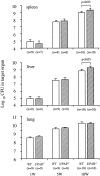
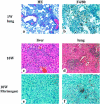
The fibrinolytic system is known to play an important role in the inflammatory response to bacterial infections. In the present study, relationships between protein components of the fibrinolytic system and infectivity by Mycobacterium avium were analyzed. Infections were initiated through noninvasive intratracheal administration of M. avium 724 in mice individually deficient for plasminogen, tissue-type plasminogen activator, urokinase-type plasminogen activator, and urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor, along with wild-type control mice. There were no differences in lung colony counts among all mouse genotypes throughout a 10-week infection. However, in tissue-type plasminogen activator and plasminogen-deficient mice an earlier dissemination of M. avium to other organs was observed. Nevertheless, the M. avium growth rates in the liver, spleen, and lung did not differ between the various mouse populations throughout a 10-week infection. Histochemical and immunohistochemical analyses at 5 and 10 weeks after infection demonstrated that plasminogen-deficient mice, compared to wild-type mice, had enhanced fibrin and fibronectin deposition, as well as increased neutrophil infiltration within liver granulomas. These results suggest that plasmin(ogen) plays a role in the turnover of extracellular matrix proteins within granulomas and has a limited effect in the early dissemination of M. avium from lungs. Thus, plasmin(ogen) functions in limiting progressive fibrosis in the granuloma during a chronic mycobacterial infection.
Figures
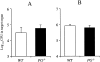
References
-
- Saunders BM, Cooper AM: Restraining mycobacteria: role of granulomas in mycobacterial infections. Immunol Cell Biol 2000, 78:334-341 - PubMed
-
- Ehlers S: Immunity to tuberculosis: a delicate balance between protection and pathology. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 1999, 23:49-58 - PubMed
-
- Castellino FJ, Ploplis VA: Plasminogen and streptokinase Bachmann F eds. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, Fibrinolytics and Antifibrinolytics 2000, vol 146:pp 25-56 Springer-Verlag, New York
-
- Lijnen HR: Plasmin and matrix metalloproteinases in vascular remodeling. Thromb Haemost 2001, 86:324-333 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

