Hepatocyte growth factor suppresses renal interstitial myofibroblast activation and intercepts Smad signal transduction
- PMID: 12875981
- PMCID: PMC1868195
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63689-9
Hepatocyte growth factor suppresses renal interstitial myofibroblast activation and intercepts Smad signal transduction
Abstract
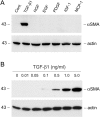
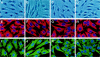
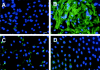
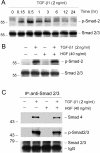
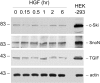
Interstitial myofibroblasts are alpha-smooth muscle actin-positive cells that play a crucial role in the accumulation of excess extracellular matrix during renal interstitial fibrogenesis. Despite their importance in the pathogenesis of renal fibrosis, relatively little is known about the regulators and the mechanism controlling the activation of renal interstitial myofibroblasts in disease conditions. Here, we show that hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) acts as a potent inhibitor of the transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1-mediated myofibroblastic activation from normal rat renal interstitial fibroblasts (NRK-49F). Simultaneous incubation of HGF abolished TGF-beta1-induced de novo alpha-smooth muscle actin expression, F-actin reorganization, and interstitial collagen I overproduction in a dose-dependent manner. To decipher the mechanism underlying HGF antagonizing TGF-beta1's action, we examined the effects of HGF on TGF-beta1-mediated Smad signaling. HGF neither inhibited Smad-2/3 phosphorylation and their association with Smad-4 induced by TGF-beta1, nor significantly affected inhibitory Smad-6 and -7 expression and cellular abundance of Smad transcriptional co-repressors in NRK-49F cells. However, pretreatment with HGF markedly attenuated activated Smad-2/3 nuclear translocation and accumulation. This action of HGF was apparently dependent on HGF-mediated extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1 and -2 (Erk-1/2) phosphorylation and activation. Inhibition of Erk-1/2 activation by Mek kinase inhibitor PD98059 restored TGF-beta1-mediated Smad-2/3 nuclear accumulation and myofibroblast activation. In vivo, HGF selectively blocked Smad-2/3 nuclear accumulation in renal interstitial cells in the fibrotic kidneys induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction. Therefore, HGF suppresses TGF-beta1-mediated renal interstitial myofibroblastic activation; and this action of HGF is likely related to a mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent blockade of Smad nuclear translocation.
Figures






Similar articles
-
A novel mechanism by which hepatocyte growth factor blocks tubular epithelial to mesenchymal transition.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005 Jan;16(1):68-78. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2003090795. Epub 2004 Nov 10. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005. PMID: 15537870
-
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D inhibits renal interstitial myofibroblast activation by inducing hepatocyte growth factor expression.Kidney Int. 2005 Oct;68(4):1500-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00562.x. Kidney Int. 2005. PMID: 16164627
-
Hepatocyte growth factor antagonizes the profibrotic action of TGF-beta1 in mesangial cells by stabilizing Smad transcriptional corepressor TGIF.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004 Jun;15(6):1402-12. doi: 10.1097/01.asn.0000130568.53923.fd. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004. PMID: 15153551
-
Hepatocyte growth factor in kidney fibrosis: therapeutic potential and mechanisms of action.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2004 Jul;287(1):F7-16. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00451.2003. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15180923 Review.
-
Central role of dysregulation of TGF-β/Smad in CKD progression and potential targets of its treatment.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 May;101:670-681. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.090. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29518614 Review.
Cited by
-
Mouse hepatic oval cells require Met-dependent PI3K to impair TGF-β-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53108. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053108. Epub 2013 Jan 2. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23301029 Free PMC article.
-
Sonic hedgehog signaling mediates epithelial-mesenchymal communication and promotes renal fibrosis.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 May;23(5):801-13. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2011060614. Epub 2012 Feb 2. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22302193 Free PMC article.
-
Opposite action of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma in regulating renal inflammation: functional switch by its ligand.J Biol Chem. 2010 Sep 24;285(39):29981-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.110908. Epub 2010 Jul 27. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20663893 Free PMC article.
-
Renal Injury during Long-Term Crizotinib Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 25;19(10):2902. doi: 10.3390/ijms19102902. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30257437 Free PMC article.
-
tPA is a potent mitogen for renal interstitial fibroblasts: role of beta1 integrin/focal adhesion kinase signaling.Am J Pathol. 2010 Sep;177(3):1164-75. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.091269. Epub 2010 Jul 16. Am J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20639453 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eddy AA: Molecular basis of renal fibrosis. Pediatr Nephrol 2000, 15:290-301 - PubMed
-
- Muchaneta-Kubara EC, el Nahas AM: Myofibroblast phenotypes expression in experimental renal scarring. Nephrol Dial Transplant 1997, 12:904-915 - PubMed
-
- Powell DW, Mifflin RC, Valentich JD, Crowe SE, Saada JI, West AB: Myofibroblasts. I. Paracrine cells important in health and disease. Am J Physiol 1999, 277:C1-C9 - PubMed
-
- Klahr S: Urinary tract obstruction. Semin Nephrol 2001, 21:133-145 - PubMed
-
- De Heer E, Sijpkens YW, Verkade M, den Dulk M, Langers A, Schutrups J, Bruijn JA, van Es LA: Morphometry of interstitial fibrosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2000, 15:72-73 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

