AP-1 mediated relief of repressive activity of the CD30 promoter microsatellite in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells
- PMID: 12875982
- PMCID: PMC1868231
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63690-5
AP-1 mediated relief of repressive activity of the CD30 promoter microsatellite in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells
Abstract
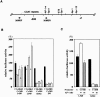
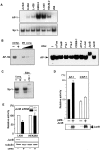
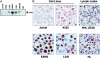
Overexpression of CD30 is the hallmark of Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg (H-RS) cells and drives constitutive nuclear factor-kappaB activation that is the molecular basis for the pathophysiology of Hodgkin's lymphoma. Transcription of the CD30 gene is controlled by the core promoter that is driven by Sp-1 and the microsatellite sequences (MSs) that represses core promoter activity. To understand the mechanism(s) of CD30 overexpression in H-RS cells, we structurally and functionally characterized the CD30 MSs. Although the CD30 MS of H-RS cell lines was polymorphic, it was not truncated compared with that of control cells. A strong core promoter activity and constitutive Sp-1 binding were revealed in all cell lines examined irrespective of the levels of CD30 expression. In transient reporter gene assays, all MS clones derived from H-RS cell lines repressed the core promoter activity in unrelated cell lines, but not in the H-RS cell lines. An AP-1-binding site was found in the MS at nucleotide position of -377 to -371, the presence of which was found to relieve repression of the core promoter in H-RS cell lines but not in other tumor cell lines. H-RS cell lines showed constitutive and strong AP-1-binding activity, but other cell lines did not. The AP-1 complex contained JunB, whose overexpression activated reporter constructs driven by the CD30 promoter including the MSs, and was dependent on the AP-1 site. JunB expression was detected in H-RS cells in vitro and in vivo, but not in reactive cells or tumor cells of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of diffuse large B-cell type. Transduction of JunB small interfering RNAs suppressed CD30 promoter activity in L428 cells but not in control cells. Taken together, overexpression and binding of JunB to the AP-1 site appear to relieve the repression of the core promoter by the CD30 MS in H-RS cells, which provide one basis for the constitutive overexpression of CD30 in Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Figures


References
-
- Gruss HJ, Kadin ME: Pathophysiology of Hodgkin’s disease: functional and molecular aspects. Baillieres Clin Haematol 1996, 9:417-446 - PubMed
-
- Cossman J, Annunziata CM, Barash S, Staudt L, Dillon P, He WW, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Rosen CA, Carter KC: Reed-Sternberg cell genome expression supports a B-cell lineage. Blood 1999, 94:411-416 - PubMed
-
- Kuppers R, Rajewsky K: The origin of Hodgkin and Reed/Sternberg cells in Hodgkin’s disease. Annu Rev Immunol 1998, 16:471-493 - PubMed
-
- Kuppers R, Rajewsky K, Zhao M, Simons G, Laumann R, Fischer R, Hansmann ML: Hodgkin disease: Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells picked from histological sections show clonal immunoglobulin gene rearrangements and appear to be derived from B cells at various stages of development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994, 91:10962-10966 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

