Diffusion barriers of tripartite sporopollenin microcapsules prepared from pine pollen
- PMID: 12876191
- PMCID: PMC4243658
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mcg136
Diffusion barriers of tripartite sporopollenin microcapsules prepared from pine pollen
Abstract
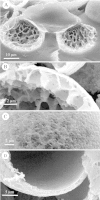
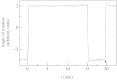
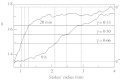
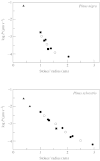
Tripartite sporopollenin microcapsules prepared from pine pollen (Pinus sylvestris L. and Pinus nigra Arnold) were analysed with respect to the permeability of the different strata of the exine which surround the gametophyte and form the sacci. The sexine at the surface of the sacci is highly permeable for polymer molecules and latex particles with a diameter of up to 200 nm, whereas the nexine covering the gametophyte is impermeable for dextran molecules, with a Stokes' radius > or =4 nm (Dextran T 70), and for the tetravalent anionic dye Evans Blue (Stokes' radius = 1.3 nm). The central capsules obtained by dissolution of the sporoplasts showed strictly membrane-controlled exchange of non-electrolytes, with half-equilibration times in the range of minutes (monosaccharides, oligosaccharides) to hours (dextran molecules with Stokes' radii up to 2.5 nm). The dependence of the permeability coefficients of the nexine for non-electrolytes on Stokes' radius or molecular weight shows that the aqueous pores through the nexine are inhomogeneous with respect to their size, and that most pores are too narrow for free diffusion of sugar molecules. To explain the barrier function of the nexine for Evans Blue, it is assumed that at least the larger pores, which enable slow permeation of dextran molecules, contain negative charges.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Water relations of the pine exine.Ann Bot. 2005 Aug;96(2):201-8. doi: 10.1093/aob/mci169. Epub 2005 May 16. Ann Bot. 2005. PMID: 15897205 Free PMC article.
-
[Analysis of pine pollen by using FTIR, SEM and energy-dispersive X-ray analysis].Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi. 2005 Nov;25(11):1797-800. Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi. 2005. PMID: 16499047 Chinese.
-
Permeability of single capillaries to intermediate-sized colored solutes.Am J Physiol. 1983 Sep;245(3):H495-505. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1983.245.3.H495. Am J Physiol. 1983. PMID: 6604463
-
Sporopollenin - Invincible biopolymer for sustainable biomedical applications.Int J Biol Macromol. 2022 Dec 1;222(Pt B):2957-2965. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.10.071. Epub 2022 Oct 13. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022. PMID: 36244536 Review.
-
The biosynthesis, composition and assembly of the outer pollen wall: A tough case to crack.Phytochemistry. 2015 May;113:170-82. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2014.05.002. Epub 2014 Jun 3. Phytochemistry. 2015. PMID: 24906292 Review.
Cited by
-
A chemical treatment method for obtaining clean and intact pollen shells of different species.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018 Jul 9;4(7):2319-2329. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.8b00304. Epub 2018 Jun 6. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018. PMID: 31106262 Free PMC article.
-
CYP703 is an ancient cytochrome P450 in land plants catalyzing in-chain hydroxylation of lauric acid to provide building blocks for sporopollenin synthesis in pollen.Plant Cell. 2007 May;19(5):1473-87. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.045948. Epub 2007 May 11. Plant Cell. 2007. PMID: 17496121 Free PMC article.
-
Hollow pollen shells to enhance drug delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2014 Mar 14;6(1):80-96. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics6010080. Pharmaceutics. 2014. PMID: 24638098 Free PMC article.
-
LAP6/POLYKETIDE SYNTHASE A and LAP5/POLYKETIDE SYNTHASE B encode hydroxyalkyl α-pyrone synthases required for pollen development and sporopollenin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Cell. 2010 Dec;22(12):4045-66. doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.080028. Epub 2010 Dec 30. Plant Cell. 2010. PMID: 21193570 Free PMC article.
-
Microwave assisted one-pot green synthesis of cinnoline derivatives inside natural sporopollenin microcapsules.RSC Adv. 2018 Jun 26;8(41):23241-23251. doi: 10.1039/c8ra04195d. eCollection 2018 Jun 21. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35540124 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AdamsonR, Gregson S, Shaw G.1983. New applications of sporopollenin as a solid phase support for peptide synthesis and the use of sonic agitation. International Journal of Peptide and Protein Research 22: 560–564. - PubMed
-
- AhlersF, Bubert H, Steuernagel S, Wiermann R.2000. The nature of oxygen in sporopollenin from the pollen of Typha angustifolia L. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung 55c: 129–136. - PubMed
-
- BaileyIW.1960. Some useful techniques in the study and interpretation of pollen morphology. Journal of Arnold Arboretum 41: 141–151.
-
- BernardsMA.2002. Demystifying suberin. Canadian Journal of Botany 80: 227–240.
-
- BlackmoreS.1990. Sporoderm homologies and morphogenesis in land plants, with a discussion of Echinops sphaerocephala (Compositae). Plant Systematics and Evolution Suppl. 5: 1–12.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

