Molecular genetics of pediatric soft tissue tumors: clinical application
- PMID: 12876204
- PMCID: PMC1907327
- DOI: 10.1016/S1525-1578(10)60466-7
Molecular genetics of pediatric soft tissue tumors: clinical application
Abstract
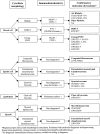
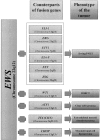
The application of molecular genetics to pediatric soft tissue tumors has grown tremendously over the last decade. It has resulted in the identification of novel genes that have provided us with an increased understanding of oncogenesis. Furthermore, these findings have identified diagnostic and potentially prognostic factors for patient management. Molecular diagnostic techniques, such as reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), have become important tools for evaluating pediatric soft tissue tumors. By detecting characteristic fusion genes, these techniques have greatly increased the diagnostic accuracy of histopathological classification. One of the exciting promises of the development of these molecular techniques is their ability to detect micrometastasis and minimal residual disease. Monitoring of minimal residual disease in pediatric soft tissue tumors by quantitative RT-PCR may provide important prognostic information. Furthermore, the potential development of targeted therapy based on the understanding of the molecular pathology of a specific soft tissue tumor may complement existing treatments and improve disease outcome.
Figures
References
-
- Raney RB: Soft-tissue sarcoma in childhood and adolescence. Curr Oncol Rep 2002, 4:291-298 - PubMed
-
- Crist WM, Anderson JR, Meza JL, Fryer C, Raney RB, Ruymann FB, Breneman J, Qualman SJ, Wiener E, Wharam M, Lobe T, Webber B, Maurer HM, Donaldson SS: Intergroup rhabdomyosarcoma study-IV: results for patients with non-metastatic disease. J Clin Oncol 2001, 19:3091-3102 - PubMed
-
- Burdach S, Jurgens H: High-dose chemoradiotherapy (HDC) in the Ewing family of tumors (EFT). Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2002, 41:169-189 - PubMed
-
- Pfeifer JD, Hill DA, O’Sullivan MJ, Dehner LP: Diagnostic gold standard for soft tissue tumours: morphology or molecular genetics? Histopathology 2000, 37:485-500 - PubMed
-
- Kilpatrick SE, Garvin AJ: Recent advances in the diagnosis of pediatric soft-tissue tumors. Med Pediatr Oncol 1999, 32:373-376 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources