Functions of fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-2 and FGF-5 in astroglial differentiation and blood-brain barrier permeability: evidence from mouse mutants
- PMID: 12878680
- PMCID: PMC6740627
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-16-06404.2003
Functions of fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-2 and FGF-5 in astroglial differentiation and blood-brain barrier permeability: evidence from mouse mutants
Abstract
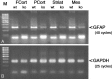
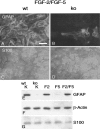
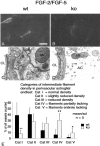
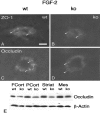
Multiple evidence suggests that fibroblast growth factors (FGFs), most prominently FGF-2, affect astroglial proliferation, maturation, and transition to a reactive phenotype in vitro, and after exogenous administration, in vivo. Whether this reflects a physiological role of endogenous FGF is unknown. Using FGF-2 and FGF-5 single- and double mutant mice we show now a region-specific reduction of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), but not of S100 in gray matter astrocytes. FGF-2 is apparently the major regulator of GFAP, because in mice deficient for FGF-2, GFAP is distinctly reduced in cortex and striatum, whereas in FGF-5-/- animals only a reduction in the midbrain tegmentum can be observed. In FGF-2-/-/FGF-5-/- double mutant animals, GFAP-immunoreactivity is reduced in all three brain regions. Cortical astrocytes cultured from FGF-2-/-/FGF-5-/- double mutant mice revealed reduced levels of GFAP, but not S100 as compared with wild-type littermates. This phenotype could be rescued by exogenous FGF-2 but not FGF-5 (10 ng/ml). Electron microscopy revealed reduced levels of intermediate filaments in perivascular astroglial endfeet. This defect was accompanied by enhanced permeability of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), as detected by albumin extravasation. Levels of the tight junction proteins Occludin and ZO-1 were reduced in blood vessels of FGF-2-/-/FGF-5-/- double mutant mice as compared with wild-type littermates. Our data support the notion that endogenous FGF-2 and FGF-5 regulate GFAP expression in a region-specific manner. The observed defect in astroglial differentiation is accompanied by a defect in BBB function arguing for an indirect or direct role of FGFs in the regulation of BBB permeability in vivo.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Fibroblast growth factors-5 and -9 distinctly regulate expression and function of the gap junction protein connexin43 in cultured astroglial cells from different brain regions.Glia. 2000 May;30(3):231-41. Glia. 2000. PMID: 10756073
-
Delayed astrocytic contact with cerebral blood vessels in FGF-2 deficient mice does not compromise permeability properties at the developing blood-brain barrier.Dev Neurobiol. 2016 Nov;76(11):1201-1212. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22383. Epub 2016 Feb 24. Dev Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26850754
-
Fibroblast growth factor 2 regulates astrocyte differentiation in a region-specific manner in the hindbrain.Glia. 2011 May;59(5):708-19. doi: 10.1002/glia.21141. Epub 2011 Feb 14. Glia. 2011. PMID: 21322057
-
Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP): modulation by growth factors and its implication in astrocyte differentiation.Braz J Med Biol Res. 1999 May;32(5):619-31. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x1999000500016. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1999. PMID: 10412574 Review.
-
Astrogliogenesis in human fetal brain: complex spatiotemporal immunoreactivity patterns of GFAP, S100, AQP4 and YKL-40.J Anat. 2019 Sep;235(3):590-615. doi: 10.1111/joa.12948. Epub 2019 Mar 22. J Anat. 2019. PMID: 30901080 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
FGF-receptor signalling controls neural cell diversity in the zebrafish hindbrain by regulating olig2 and sox9.Development. 2010 Jan;137(1):33-42. doi: 10.1242/dev.038026. Development. 2010. PMID: 20023158 Free PMC article.
-
FGF5 as an oncogenic factor in human glioblastoma multiforme: autocrine and paracrine activities.Oncogene. 2008 Jul 10;27(30):4180-90. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.61. Epub 2008 Mar 24. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 18362893 Free PMC article.
-
The Three Sisters of Fate in Multiple Sclerosis: Klotho (Clotho), Fibroblast Growth Factor-23 (Lachesis), and Vitamin D (Atropos).Ann Neurosci. 2016 Sep;23(3):155-161. doi: 10.1159/000449181. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Ann Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27721584 Free PMC article.
-
"You Shall Not Pass"-tight junctions of the blood brain barrier.Front Neurosci. 2014 Dec 3;8:392. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2014.00392. eCollection 2014. Front Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25520612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptors 1 and 2 in keratinocytes control the epidermal barrier and cutaneous homeostasis.J Cell Biol. 2010 Mar 22;188(6):935-52. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200910126. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20308431 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Batter DK, Corpina RA, Roy C, Spray DC, Hertzberg EL, Kessler JA ( 1992) Heterogeneity in gap junction expression in astrocytes cultured from different brain regions. Glia 6: 213-221. - PubMed
-
- Biegel D, Spencer DD, Pachter JS ( 1995) Isolation and culture of human brain microvessel endothelial cells for the study of blood-brain barrier properties in vitro. Brain Res 692: 183-189. - PubMed
-
- Bieger S, Unsicker K ( 1996) Functions of fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) in the nervous system. In: Chemical factors in neural growth, degeneration and repair (Bell C, ed), pp 339-375. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
-
- Bignami A, Eng LF, Dahl D, Uyeda CT ( 1972) Localization of the glial fibrillary acidic protein in astrocytes by immunofluorescence. Brain Res 43: 429-435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
