Biosynthesis of isoprenoids: crystal structure of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase
- PMID: 12878729
- PMCID: PMC170891
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1533425100
Biosynthesis of isoprenoids: crystal structure of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase
Abstract
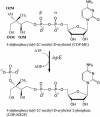
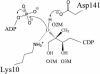
4-Diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-d-erythritol kinase, an essential enzyme in the nonmevalonate pathway of isopentenyl diphosphate and dimethylallyl diphosphate biosynthesis, catalyzes the single ATP-dependent phosphorylation stage affording 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-d-erythritol-2-phosphate. The 2-A resolution crystal structure of the Escherichia coli enzyme in a ternary complex with substrate and a nonhydrolyzable ATP analogue reveals the molecular determinants of specificity and catalysis. The enzyme subunit displays the alpha/beta fold characteristic of the galactose kinase/homoserine kinase/mevalonate kinase/phosphomevalonate kinase superfamily, arranged into cofactor and substrate-binding domains with the catalytic center positioned in a deep cleft between domains. Comparisons with related members of this superfamily indicate that the core regions of each domain are conserved, whereas there are significant differences in the substrate-binding pockets. The nonmevalonate pathway is essential in many microbial pathogens and distinct from the mevalonate pathway used by mammals. The high degree of sequence conservation of the enzyme across bacterial species suggests similarities in structure, specificity, and mechanism. Our model therefore provides an accurate template to facilitate the structure-based design of broad-spectrum antimicrobial agents.
Figures


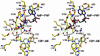
Similar articles
-
Characterization of Aquifex aeolicus 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-d-erythritol kinase - ligand recognition in a template for antimicrobial drug discovery.FEBS J. 2008 Jun;275(11):2779-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06418.x. Epub 2008 Apr 16. FEBS J. 2008. PMID: 18422643 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase (IspE) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.FASEB J. 2011 May;25(5):1577-84. doi: 10.1096/fj.10-175786. Epub 2011 Jan 31. FASEB J. 2011. PMID: 21282208
-
A triclinic crystal form of Escherichia coli 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase and reassessment of the quaternary structure.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2010 Mar 1;66(Pt 3):237-41. doi: 10.1107/S1744309109054591. Epub 2010 Feb 23. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2010. PMID: 20208151 Free PMC article.
-
Development of inhibitors of the 2C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) pathway enzymes as potential anti-infective agents.J Med Chem. 2014 Dec 11;57(23):9740-63. doi: 10.1021/jm5010978. Epub 2014 Sep 25. J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25210872 Review.
-
Structure and reactivity in the non-mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis.Biochem Soc Trans. 2003 Jun;31(Pt 3):537-42. doi: 10.1042/bst0310537. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003. PMID: 12773152 Review.
Cited by
-
IspE inhibitors identified by a combination of in silico and in vitro high-throughput screening.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35792. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035792. Epub 2012 Apr 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22563402 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and characterization of soluble 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase from bacterial pathogens.Chem Biol. 2009 Dec 24;16(12):1230-9. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2009.10.014. Chem Biol. 2009. PMID: 20064433 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetic and functional analysis of L-threonine kinase, the PduX enzyme of Salmonella enterica.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jul 24;284(30):20240-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.027425. Epub 2009 Jun 9. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19509296 Free PMC article.
-
Two copies of 4-(cytidine 5'-diphospho)-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase (CMK) gene in Ginkgo biloba: molecular cloning and functional characterization.Planta. 2008 Nov;228(6):941-50. doi: 10.1007/s00425-008-0794-1. Epub 2008 Jul 31. Planta. 2008. PMID: 18668260
-
Absence of substrate channeling between active sites in the Agrobacterium tumefaciens IspDF and IspE enzymes of the methyl erythritol phosphate pathway.Biochemistry. 2006 Mar 21;45(11):3548-53. doi: 10.1021/bi0520075. Biochemistry. 2006. PMID: 16533036 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sacchettini, J. C. & Poulter, C. D. (1997) Science 277, 1788–1789. - PubMed
-
- Rohmer, M. (1999) in Comprehensive Natural Products Chemistry: Isoprenoids Including Carotenoids and Sterols, ed. Cane, D. (Elsevier, Amsterdam), Vol. 2, pp. 45–67.
-
- Beytia, E. D. & Porter, J. W. (1976) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 45, 113–142. - PubMed
-
- Edwards, P. A. & Ericsson, J. (1999) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 68, 157–185. - PubMed
-
- Boucher, Y. & Doolittle, W. F. (2000) Mol. Microbiol. 37, 703–716. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

