Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence by quorum sensing inhibitors
- PMID: 12881415
- PMCID: PMC169039
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg366
Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence by quorum sensing inhibitors
Abstract
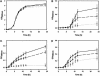
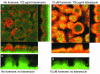
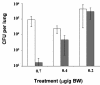
Traditional treatment of infectious diseases is based on compounds that kill or inhibit growth of bacteria. A major concern with this approach is the frequent development of resistance to antibiotics. The discovery of communication systems (quorum sensing systems) regulating bacterial virulence has afforded a novel opportunity to control infectious bacteria without interfering with growth. Compounds that can override communication signals have been found in the marine environment. Using Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 as an example of an opportunistic human pathogen, we show that a synthetic derivate of natural furanone compounds can act as a potent antagonist of bacterial quorum sensing. We employed GeneChip microarray technology to identify furanone target genes and to map the quorum sensing regulon. The transcriptome analysis showed that the furanone drug specifically targeted quorum sensing systems and inhibited virulence factor expression. Application of the drug to P.aeruginosa biofilms increased bacterial susceptibility to tobramycin and SDS. In a mouse pulmonary infection model, the drug inhibited quorum sensing of the infecting bacteria and promoted their clearance by the mouse immune response.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

