The apolipoprotein B mRNA editing complex performs a multifunctional cycle and suppresses nonsense-mediated decay
- PMID: 12881431
- PMCID: PMC169042
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg369
The apolipoprotein B mRNA editing complex performs a multifunctional cycle and suppresses nonsense-mediated decay
Abstract
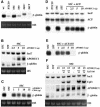
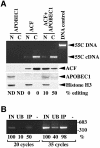
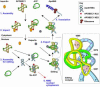
The C to U editing of apolipoprotein B (apoB) mRNA is mediated by a minimal complex composed of an RNA-binding cytidine deaminase (APOBEC1) and a complementing specificity factor (ACF). This editing generates a premature termination codon and a truncated open reading frame. We demonstrate that the APOBEC1-ACF holoenzyme mediates a multifunctional cycle. The atypical APOBEC1 nuclear localization signal is involved in RNA binding and is used to import ACF into the nucleus as cargo. APOBEC1 alone induces nonsense-mediated decay (NMD). The APOBEC1-ACF complex edits and remains associated with the edited RNA to protect it from NMD. The APOBEC1 nuclear export signal is involved in the export of ACF and the edited apoB mRNA together, to the site of translation.
Figures
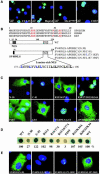
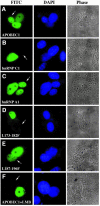
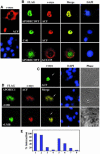
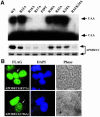
References
-
- Blanc V., Navaratnam,N., Henderson,J.O., Anant,S., Kennedy,S., Jarmuz,A., Scott,J. and Davidson,N.O. (2001a) Identification of GRY-RBP as an apolipoprotein B RNA-binding protein that interacts with both apobec-1 and apobec-1 complementation factor to modulate C to U editing. J. Biol. Chem., 276, 10272–10283. - PubMed
-
- Blanc V., Henderson,J.O., Kennedy,S. and Davidson,N.O. (2001b) Mutagenesis of apobec-1 complementation factor reveals distinct domains that modulate RNA binding, protein–protein interaction with apobec-1 and complementation of C to U RNA-editing activity. J. Biol. Chem., 276, 46386–46393. - PubMed
-
- Chester A., Scott,J., Anant,S. and Navaratnam,N. (2000) RNA editing: cytidine to uridine conversion in apolipoprotein B mRNA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1494, 1–13. - PubMed
-
- Conti E., Uy,M., Leighton,L., Blobel,G. and Kuriyan,J. (1998) Crystallographic analysis of the recognition of a nuclear localization signal by the nuclear import factor karyopherin α. Cell, 94, 193–204. - PubMed
-
- Dingwall C. and Laskey,R. (1991) Nuclear targeting sequences—a consensus? Trends Biochem. Sci., 16, 478–481. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

