Permanent cell cycle exit in G2 phase after DNA damage in normal human fibroblasts
- PMID: 12881433
- PMCID: PMC169060
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg387
Permanent cell cycle exit in G2 phase after DNA damage in normal human fibroblasts
Abstract
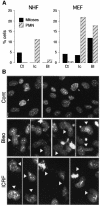
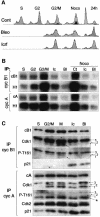
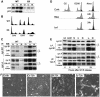
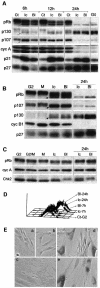
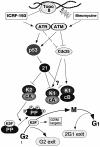
Although the Cdk inhibitor p21(Waf1/Cip1), one of the transcriptional targets of p53, has been implicated in the maintenance of G(2) arrest after DNA damage, its function at this stage of the cell cycle is not really understood. Here, we show that the exposure of normal human fibroblasts (NHFs) to genotoxic agents provokes permanent cell cycle exit in G(2) phase, whereas mouse embryo fibroblasts and transformed human cells progress through mitosis and arrest in G(1) without intervening cytokinesis. p21(Waf1/Cip1) exerts a key role in driving this G(2) exit both by inhibiting cyclin B1-Cdk1 and cyclin A-Cdk1/2 complexes, which control G(2)/M progression, and by blocking the phosphorylation of pRb family proteins. NHFs with compromised pRb proteins could still efficiently arrest in G(2) but were unable to exit the cell cycle, resulting in cell death. Our experiments show that, when under continuous genotoxic stress, normal cells can reverse their commitment to mitotic progression due to passage through the restriction point and that mechanisms involving p21(Waf1/Cip1) and pocket proteins can induce exit in G(2) and G(1).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Deregulation of p53/p21Cip1/Waf1 pathway contributes to polyploidy and apoptosis of E1A+cHa-ras transformed cells after gamma-irradiation.Oncogene. 1999 Oct 7;18(41):5611-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202945. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10523840
-
p21-Mediated nuclear retention of cyclin B1-Cdk1 in response to genotoxic stress.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Sep;15(9):3965-76. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-12-0871. Epub 2004 Jun 4. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15181148 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperoxia induces S-phase cell-cycle arrest and p21(Cip1/Waf1)-independent Cdk2 inhibition in human carcinoma T47D-H3 cells.Exp Cell Res. 2000 May 1;256(2):347-57. doi: 10.1006/excr.2000.4844. Exp Cell Res. 2000. PMID: 10772807
-
[Cell cycle regulation after exposure to ionizing radiation].Bull Cancer. 1999 Apr;86(4):345-57. Bull Cancer. 1999. PMID: 10341340 Review. French.
-
p21Cip1/Waf1 protein and its function based on a subcellular localization [corrected].J Cell Biochem. 2011 Dec;112(12):3502-6. doi: 10.1002/jcb.23296. J Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21815189 Review.
Cited by
-
A non-genetic, cell cycle-dependent mechanism of platinum resistance in lung adenocarcinoma.Elife. 2021 May 13;10:e65234. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65234. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33983115 Free PMC article.
-
The p21-dependent radiosensitization of human breast cancer cells by MLN4924, an investigational inhibitor of NEDD8 activating enzyme.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e34079. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034079. Epub 2012 Mar 22. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22457814 Free PMC article.
-
c-Jun-deficient cells undergo premature senescence as a result of spontaneous DNA damage accumulation.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Oct;24(20):9006-18. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.20.9006-9018.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15456874 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of cellular senescence in renal diseases.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Feb;24(3):2087-2097. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14952. Epub 2020 Jan 8. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31916698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear translocation of Cyclin B1 marks the restriction point for terminal cell cycle exit in G2 phase.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(17):2733-43. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2015.945831. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 25486360 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham R.T. (2001) Cell cycle checkpoint signaling through the ATM and ATR kinases. Genes Dev., 15, 2177–2196. - PubMed
-
- Andreassen P.R., Lacroix,F.B., Lohez,O.D. and Margolis,R.L. (2001a) Neither p21(WAF1) nor 14-3-3σ prevents G2 progression to mitotic catastrophe in human colon carcinoma cells after DNA damage, but p21WAF1 induces stable G1 arrest in resulting tetraploid cells. Cancer Res., 61, 7660–7668. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

