p21WAF1/CIP1 is more effective than p53 in growth suppression of mouse renal carcinoma cell line Renca in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 12884025
- PMCID: PMC12161978
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-003-0458-2
p21WAF1/CIP1 is more effective than p53 in growth suppression of mouse renal carcinoma cell line Renca in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
Purpose: Although there are many controversial reports about the effect of p53 and p21(WAF1/CIP1) overexpression in different human tumor cells, the p53 gene is shown to be a more effective candidate for cancer gene therapy because of its more pronounced ability to induce apoptosis. In the present study, we present the effect of p53 and p21(WAF1/CIP1) overexpression on mouse renal carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo.
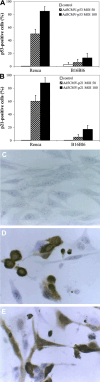
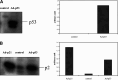
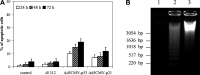
Methods: p53 and p21(WAF1/CIP1) genes were introduced into Renca cells using adenoviral vectors (Ad5CMV-p53 and Ad5CMV-p21). The induction of apoptosis was measured using Annexin V assay and DNA fragmentation analysis. The expression of proteins was examined using immunocytochemistry and Western blot methods. The ability of adenoviral vectors to inhibit tumorigenicity of Renca cells, as well as the growth of pre-established tumors was measured.
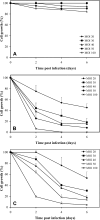
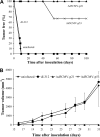
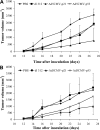
Results: In vitro growth assays revealed higher growth suppression after Ad5CMV-p21 infection. Although both vectors induced apoptosis, Ad5CMV-p53 was slightly more efficient. In vivo studies in Balb/c mice, demonstrated that tumorigenicity was completely suppressed by Ad5CMV-p21. Besides this, Ad5CMV-p21 significantly inhibited the growth of established tumors, while Ad5CMV-p53 did not.
Conclusions: These data suggest that p21(WAF1/CIP1) is a more potent growth suppressor than p53 of mouse tumor cells Renca. The divergent responses of tumor cells to p21(WAF1/CIP1) overexpression could be due to various networks that differ between species.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Status of p53 phosphorylation and function in sensitive and resistant human cancer models exposed to platinum-based DNA damaging agents.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2003 Dec;129(12):709-18. doi: 10.1007/s00432-003-0480-4. Epub 2003 Sep 26. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2003. PMID: 14513366 Free PMC article.
-
Adenoviral-mediated gene therapy with Ad5CMVp53 and Ad5CMVp21 in combination with standard therapies in human breast cancer cell lines.Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2000 Oct;30(4):395-405. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2000. PMID: 11045764
-
Different apoptotic activity and p21(WAF1/CIP1), but not p27(Kip1), expression in serrated adenomas as compared with traditional adenomas and hyperplastic polyps of the colorectum.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2003 Aug;129(8):449-55. doi: 10.1007/s00432-003-0478-y. Epub 2003 Jul 15. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12884030 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
Cited by
-
Prognostic markers in renal cell carcinoma: A focus on the 'mammalian target of rapamycin' pathway.Arab J Urol. 2012 Jun;10(2):110-7. doi: 10.1016/j.aju.2012.02.005. Epub 2012 Apr 9. Arab J Urol. 2012. PMID: 26558012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rebamipide inhibits gastric cancer cell growth.Dig Dis Sci. 2007 Jan;52(1):240-7. doi: 10.1007/s10620-006-9226-x. Epub 2006 Dec 14. Dig Dis Sci. 2007. PMID: 17171453
-
Adenovirally mediated p53 overexpression diversely influence the cell cycle of HEp-2 and CAL 27 cell lines upon cisplatin and methotrexate treatment.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2009 Dec;135(12):1747-61. doi: 10.1007/s00432-009-0621-5. Epub 2009 Jun 23. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19548002 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cardinali M, Jakus J, Shah S, Ensley JF, Robbins KC, Yeudall WA (1998) p21(WAF1/CIP1) retards the growth of human squamous cell carcinomas in vivo. Oral Oncol 34:211–218 - PubMed
-
- Clayman GL, Liu TJ, Overholt SM, Mobley SR, Wang M, Janot F, Goepfert H (1996) Gene therapy for head and neck cancer. Comparing the tumor suppressor gene p53 and a cell cycle regulator WAF1/CIP1 (p21). Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 122:489–493 - PubMed
-
- D'Orazi G, Marchetti A, Crescenzi M, Coen S, Sacchi A, Soddu S (2000) Exogenous wt-p53 protein is active in transformed cells but not in their non-transformed counterparts: implications for cancer gene therapy without tumor targeting. J Gene Med 2:11–21 - PubMed
-
- Dotto GP (2000) P21WAF1/CIP1: more than a break to the cell cycle. Biochim Biophys Acta 1471:M43-M56 - PubMed
-
- Duttaroy A, Qian J-F, Smith JS, Wang E (1997) Up-regulated p21CIP1 expression is part of the regulation quantitatively controlling serum deprivation-induced apoptosis. J Cell Biochem 64:434–446 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

