The unbinding of ATP from F1-ATPase
- PMID: 12885621
- PMCID: PMC1303195
- DOI: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74513-5
The unbinding of ATP from F1-ATPase
Abstract
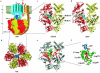
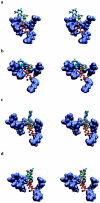
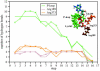
Using molecular dynamics, we study the unbinding of ATP in F(1)-ATPase from its tight binding state to its weak binding state. The calculations are made feasible through use of interpolated atomic structures from Wang and Oster [Nature 1998, 396: 279-282]. These structures are applied to atoms distant from the catalytic site. The forces from these distant atoms gradually drive a large primary region through a series of sixteen equilibrated steps that trace the hinge bending conformational change in the beta-subunit that drives rotation of gamma-subunit. As the rotation progresses, we find a sequential weakening and breaking of the hydrogen bonds between the ATP molecule and the alpha- and beta-subunits of the ATPase. This finding agrees with the "binding-zipper" model [Oster and Wang, BIOCHIM: Biophys. Acta 2000, 1458: 482-510.] In this model, the progressive formation of the hydrogen bonds is the energy source driving the rotation of the gamma-shaft during hydrolysis. Conversely, the corresponding sequential breaking of these bonds is driven by rotation of the shaft during ATP synthesis. Our results for the energetics during rotation suggest that the nucleotide's coordination with Mg(2+) during binding and release is necessary to account for the observed high efficiency of the motor.
Figures



References
-
- Abrahams, J. P., A. G. W. Leslie, and J. E. Walker. 1994. Structure at 2.8-angstrom resolution of F1-ATPase from bovine heart-mitochondria. Nature. 370:621–628. - PubMed
-
- Böckmann, R. A., and H. Grubmüller. 2002. Nanoseconds molecular dynamics simulation of primary mechanical energy transfer steps in F1-ATP synthase. Nat. Struct. Biol. 9:198–202. - PubMed
-
- Boyer, P. D. 1993. The binding change mechanism for ATP synthase - some probabilities and possibilities. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1140:215–250. - PubMed
-
- Boyer, P. D. 1997. The ATP synthase - A splendid molecular machine. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 66:717–749. - PubMed
-
- Brooks, B. R., R. E. Buccoleri, B. D. Olafson, D. J. States, S. Swaminathan, and M. Karplus. 1983. CHARMM - A program for macromolecular energy, minimization, and dynamics calculations. J. Comput. Chem. 4:187–217.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

