Vav1 phosphorylation is induced by beta2 integrin engagement on natural killer cells upstream of actin cytoskeleton and lipid raft reorganization
- PMID: 12885870
- PMCID: PMC2194094
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20021995
Vav1 phosphorylation is induced by beta2 integrin engagement on natural killer cells upstream of actin cytoskeleton and lipid raft reorganization
Abstract
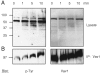
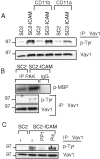
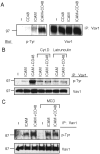
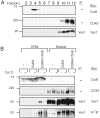
The guanine nucleotide exchange factor Vav1 regulates actin polymerization and contributes to cytotoxicity by natural killer (NK) cells. An open question is how Vav1 becomes activated and what receptor can signal upstream of actin cytoskeleton rearrangement upon NK cell contact with target cells. Using transfected insect cells that express ligands of human NK cell receptors, we show that engagement of the beta2 integrin LFA-1 on NK cells by intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 led to a tyrosine phosphorylation of Vav1 that was not sensitive to cholesterol depletion and to inhibition of actin polymerization. Vav1 phosphorylation was blocked by an inhibitor of Src-family kinases, and correlated with activation of its downstream effector PAK. Binding of activation receptor 2B4 to its ligand CD48 was not sufficient for Vav1 phosphorylation. However, coengagement of 2B4 with LFA-1 resulted in an enhancement of Vav1 phosphorylation that was sensitive to cholesterol depletion and to inhibition of actin polymerization. Vav1 was recruited to a detergent-resistant membrane (DRM) fraction only when 2B4 and LFA-1 were coengaged, but not after LFA-1 engagement. Therefore, binding of LFA-1 to ICAM-1 on target cells may initiate an early signaling cascade in NK cells through activation of Vav1, leading to cytoskeleton reorganization and amplification of signals from other activation receptors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Natural killer cell inhibitory receptors block actin cytoskeleton-dependent recruitment of 2B4 (CD244) to lipid rafts.J Exp Med. 2003 Jan 6;197(1):77-85. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020427. J Exp Med. 2003. PMID: 12515815 Free PMC article.
-
In contrast to anti-tumor activity, YT cell and primary NK cell cytotoxicity for Cryptococcus neoformans bypasses LFA-1.Int Immunol. 2009 Apr;21(4):423-32. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxp010. Epub 2009 Mar 4. Int Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19261694
-
Vav1/Rac-dependent actin cytoskeleton reorganization is required for lipid raft clustering in T cells.J Cell Biol. 2001 Oct 29;155(3):331-8. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200107080. Epub 2001 Oct 29. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11684704 Free PMC article.
-
Vav-family proteins in T-cell signalling.Curr Opin Immunol. 2005 Jun;17(3):267-74. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2005.04.003. Curr Opin Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15886116 Review.
-
Vav links antigen-receptor signaling to the actin cytoskeleton.Semin Immunol. 1998 Aug;10(4):317-27. doi: 10.1006/smim.1998.0124. Semin Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9695188 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid Raft is required for PSGL-1 ligation induced HL-60 cell adhesion on ICAM-1.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 3;8(12):e81807. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081807. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24312591 Free PMC article.
-
The adaptor protein Crk controls activation and inhibition of natural killer cells.Immunity. 2012 Apr 20;36(4):600-11. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.03.007. Epub 2012 Mar 29. Immunity. 2012. PMID: 22464172 Free PMC article.
-
Cytolytic granule polarization and degranulation controlled by different receptors in resting NK cells.J Exp Med. 2005 Oct 3;202(7):1001-12. doi: 10.1084/jem.20051143. J Exp Med. 2005. PMID: 16203869 Free PMC article.
-
Vav protein guanine nucleotide exchange factor regulates CD36 protein-mediated macrophage foam cell formation via calcium and dynamin-dependent processes.J Biol Chem. 2011 Oct 14;286(41):36011-36019. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.265082. Epub 2011 Aug 24. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21865158 Free PMC article.
-
Dendritic cell and natural killer cell cross-talk: a pivotal role of CX3CL1 in NK cytoskeleton organization and activation.Blood. 2008 Dec 1;112(12):4420-4. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-12-126888. Epub 2008 Aug 5. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18682600 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moretta, A., C. Bottino, M. Vitale, D. Pende, C. Cantoni, M.C. Mingari, R. Biassoni, and L. Moretta. 2001. Activating receptors and coreceptors involved in human natural killer cell-mediated cytolysis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 19:197–223. - PubMed
-
- Cerwenka, A., and L.L. Lanier. 2001. Natural killer cells, viruses, and cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 1:41–49. - PubMed
-
- Diefenbach, A., E. Tomasello, M. Lucas, A.M. Jamieson, J.K. Hsia, E. Vivier, and D.H. Raulet. 2002. Selective associations with signaling proteins determine stimulatory versus costimulatory activity of NKG2D. Nat. Immunol. 3:1142–1149. - PubMed
-
- Gilfillan, S., E.L. Ho, M. Cella, W.M. Yokoyama, and M. Colonna. 2002. NKG2D recruits two distinct adapters to trigger NK cell activation and costimulation. Nat. Immunol. 3:1150–1155. - PubMed
-
- Colucci, F., E. Schweighoffer, E. Tomasello, M. Turner, J.R. Ortaldo, E. Vivier, V.L. Tybulewicz, and J.P. Di Santo. 2002. Natural cytotoxicity uncoupled from the Syk and ZAP-70 intracellular kinases. Nat. Immunol. 3:288–294. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

