Induction of protective immune responses against R5 human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection in hu-PBL-SCID mice by intrasplenic immunization with HIV-1-pulsed dendritic cells: possible involvement of a novel factor of human CD4(+) T-cell origin
- PMID: 12885891
- PMCID: PMC167224
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.16.8719-8728.2003
Induction of protective immune responses against R5 human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection in hu-PBL-SCID mice by intrasplenic immunization with HIV-1-pulsed dendritic cells: possible involvement of a novel factor of human CD4(+) T-cell origin
Abstract
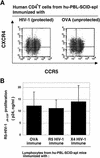
The potential of a dendritic cell (DC)-based vaccine against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection in humans was explored with SCID mice reconstituted with human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). HIV-1-negative normal human PBMC were transplanted directly into the spleens of SCID mice (hu-PBL-SCID-spl mice) together with autologous mature DCs pulsed with either inactivated HIV-1 (strain R5 or X4) or ovalbumin (OVA), followed by a booster injection 5 days later with autologous DCs pulsed with the same respective antigens. Five days later, these mice were challenged intraperitoneally with R5 HIV-1(JR-CSF). Analysis of infection at 7 days postinfection showed that the DC-HIV-1-immunized hu-PBL-SCID-spl mice, irrespective of the HIV-1 isolate used for immunization, were protected against HIV-1 infection. In contrast, none of the DC-OVA-immunized mice were protected. Sera from the DC-HIV-1- but not the DC-OVA-immunized mice inhibited the in vitro infection of activated PBMC and macrophages with R5, but not X4, HIV-1. Upon restimulation with HIV-1 in vitro, the human CD4(+) T cells derived from the DC-HIV-1-immunized mice produced a similar R5 HIV-1 suppressor factor. Neutralizing antibodies against human RANTES, MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta, alpha interferon (IFN-alpha), IFN-beta, IFN-gamma, interleukin-4 (IL-4), IL-10, IL-13, IL-16, MCP-1, MCP-3, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), or TNF-beta failed to reverse the HIV-1-suppressive activity. These results show that inactivated HIV-1-pulsed autologous DCs can stimulate splenic resident human CD4(+) T cells in hu-PBL-SCID-spl mice to produce a yet-to-be-defined, novel soluble factor(s) with protective properties against R5 HIV-1 infection.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Identification of HIV-1 epitopes that induce the synthesis of a R5 HIV-1 suppression factor by human CD4+ T cells isolated from HIV-1 immunized hu-PBL SCID mice.Clin Dev Immunol. 2005 Dec;12(4):235-42. doi: 10.1080/17402520500391557. Clin Dev Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16584108 Free PMC article.
-
Potent immune response against HIV-1 and protection from virus challenge in hu-PBL-SCID mice immunized with inactivated virus-pulsed dendritic cells generated in the presence of IFN-alpha.J Exp Med. 2003 Jul 21;198(2):361-7. doi: 10.1084/jem.20021924. J Exp Med. 2003. PMID: 12874266 Free PMC article.
-
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 strains R5 and X4 induce different pathogenic effects in hu-PBL-SCID mice, depending on the state of activation/differentiation of human target cells at the time of primary infection.J Virol. 1999 Aug;73(8):6453-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.8.6453-6459.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10400739 Free PMC article.
-
Dendritic cells and the promise of therapeutic vaccines for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1.Curr HIV Res. 2003 Apr;1(2):205-16. doi: 10.2174/1570162033485285. Curr HIV Res. 2003. PMID: 15043203 Review.
-
[Model of viral infection in SCID mice: SCID-hu mouse and hu-PBL-SCID mouse].Uirusu. 1999 Jun;49(1):33-9. doi: 10.2222/jsv.49.33. Uirusu. 1999. PMID: 10548937 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Animal models for HIV/AIDS research.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012 Dec;10(12):852-67. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2911. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23154262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD8+ cell depletion accelerates HIV-1 immunopathology in humanized mice.J Immunol. 2010 Jun 15;184(12):7082-91. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000438. Epub 2010 May 21. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20495069 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of robust immune responses against human immunodeficiency virus is supported by the inherent tropism of adeno-associated virus type 5 for dendritic cells.J Virol. 2006 Dec;80(24):11899-910. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00890-06. Epub 2006 Sep 27. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 17005662 Free PMC article.
-
A Potential of an Anti-HTLV-I gp46 Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody (LAT-27) for Passive Immunization against Both Horizontal and Mother-to-Child Vertical Infection with Human T Cell Leukemia Virus Type-I.Viruses. 2016 Feb 3;8(2):41. doi: 10.3390/v8020041. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 26848684 Free PMC article.
-
Can immunotherapy be useful as a "functional cure" for infection with Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1?Retrovirology. 2012 Sep 7;9:72. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-9-72. Retrovirology. 2012. PMID: 22958464 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bombil, F., J. P. Kints, J. M. Scheiff, H. Bazin, and D. Latinne. 1996. A promising model of primary human immunization in human-scid mouse. Immunobiology 195:360-375. - PubMed
-
- Delhem, N., F. Hadida, G. Gorochov, F. Carpentier, J. P. de Cavel, J. F. Andreani, B. Autran, and J. Y. Cesbron. 1998. Primary Th1 cell immunization against HIVgp160 in SCID-hu mice coengrafted with peripheral blood lymphocytes and skin. J. Immunol. 161:2060-2069. - PubMed
-
- Dhawan, S., L. M. Wahl, A. Heredia, Y. Zhang, J. S. Epstein, M. S. Meltzer, and I. K. Hewlett. 1995. Interferon-gamma inhibits HIV-induced invasiveness of monocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 58:713-716. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

