Reovirus-induced alteration in expression of apoptosis and DNA repair genes with potential roles in viral pathogenesis
- PMID: 12885910
- PMCID: PMC167209
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.16.8934-8947.2003
Reovirus-induced alteration in expression of apoptosis and DNA repair genes with potential roles in viral pathogenesis
Abstract
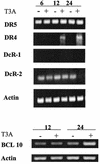
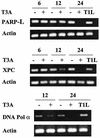
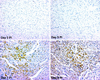
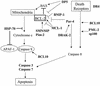
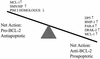
Reoviruses are a leading model for understanding cellular mechanisms of virus-induced apoptosis. Reoviruses induce apoptosis in multiple cell lines in vitro, and apoptosis plays a key role in virus-induced tissue injury of the heart and brain in vivo. The activation of transcription factors NF-kappaB and c-Jun are key events in reovirus-induced apoptosis, indicating that new gene expression is critical to this process. We used high-density oligonucleotide microarrays to analyze cellular transcriptional alterations in HEK293 cells after infection with reovirus strain T3A (i.e., apoptosis inducing) compared to infection with reovirus strain T1L (i.e., minimally apoptosis inducing) and uninfected cells. These strains also differ dramatically in their potential to induce apoptotic injury in hearts of infected mice in vivo-T3A is myocarditic, whereas T1L is not. Using high-throughput microarray analysis of over 12,000 genes, we identified differential expression of a defined subset of genes involved in apoptosis and DNA repair after reovirus infection. This provides the first comparative analysis of altered gene expression after infection with viruses of differing apoptotic phenotypes and provides insight into pathogenic mechanisms of virus-induced disease.
Figures
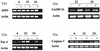

Similar articles
-
Reovirus infection activates JNK and the JNK-dependent transcription factor c-Jun.J Virol. 2001 Dec;75(23):11275-83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.23.11275-11283.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11689607 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of reovirus-induced cell death and tissue injury: role of apoptosis and virus-induced perturbation of host-cell signaling and transcription factor activation.Viral Immunol. 2005;18(1):89-115. doi: 10.1089/vim.2005.18.89. Viral Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15802955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reovirus receptors, cell entry, and proapoptotic signaling.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;790:42-71. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-7651-1_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23884585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reovirus activates a caspase-independent cell death pathway.mBio. 2013 May 14;4(3):e00178-13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00178-13. mBio. 2013. PMID: 23674612 Free PMC article.
-
Reovirus-Induced Apoptosis in the Intestine Limits Establishment of Enteric Infection.J Virol. 2018 Apr 27;92(10):e02062-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02062-17. Print 2018 May 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29514905 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
PUMA and NF-kB Are Cell Signaling Predictors of Reovirus Oncolysis of Breast Cancer.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 18;12(1):e0168233. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168233. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28099441 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of the host response proteome after mammalian reovirus T1L infection.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51939. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051939. Epub 2012 Dec 11. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23240068 Free PMC article.
-
Regulators of global genome repair do not respond to DNA damaging therapy but correlate with survival in melanoma.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 5;8(8):e70424. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070424. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23940574 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Translation of Viral mRNA in Reovirus-Infected Cells: Progress and Remaining Questions.Viruses. 2018 Nov 27;10(12):671. doi: 10.3390/v10120671. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30486370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of apoptosis during reovirus infection.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005;289:1-24. doi: 10.1007/3-540-27320-4_1. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15791949 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baghdiguian, S., M. Martin, I. Richard, F. Pons, C. Astier, N. Bourg, R. T. Hay, R. Chemaly, G. Halaby, J. Loiselet, L. V. Anderson, D. M. Lopez, M. Fardeau, P. Mangeat, J. S. Beckmann, and G. Lefranc. 1999. Calpain 3 deficiency is associated with myonuclear apoptosis and profound perturbation of the IκB α/NF-κB pathway in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A. Nat. Med. 5:503-511. - PubMed
-
- Baytel, D., S. Shalom, I. Madgar, R. Weissenberg, and J. Don. 1998. The human Pim-2 proto-oncogene and its testicular expression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1442:274-285. (Erratum, 1444:312-313, 1999.) - PubMed
-
- Beere, H. M., B. B. Wolf, K. Cain, D. D. Mosser, A. Mahboubi, T. Kuwana, P. Tailor, R. I. Morimoto, G. M. Cohen, and D. R. Green. 2000. Heat-shock protein 70 inhibits apoptosis by preventing recruitment of procaspase-9 to the Apaf-1 apoptosome. Nat. Cell Biol. 2:469-475. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

