Conditional suppression of cellular genes: lentivirus vector-mediated drug-inducible RNA interference
- PMID: 12885912
- PMCID: PMC167245
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.16.8957-8951.2003
Conditional suppression of cellular genes: lentivirus vector-mediated drug-inducible RNA interference
Abstract
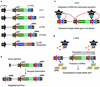
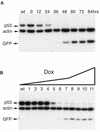
RNA interference has emerged as a powerful technique to downregulate the expression of specific genes in cells and in animals, thus opening new perspectives in fields ranging from developmental genetics to molecular therapeutics. Here, we describe a method that significantly expands the potential of RNA interference by permitting the conditional suppression of genes in mammalian cells. Within a lentivirus vector background, we subjected the polymerase III promoter-dependent production of small interfering RNAs to doxycycline-controllable transcriptional repression. The resulting system can achieve the highly efficient and completely drug-inducible knockdown of cellular genes. As lentivirus vectors can stably transduce a wide variety of targets both in vitro and in vivo and can be used to generate transgenic animals, the present system should have broad applications.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Doxycycline-dependent inducible and reversible RNA interference mediated by a single lentivirus vector.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2013;77(4):776-81. doi: 10.1271/bbb.120917. Epub 2013 Apr 7. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23563548
-
Tuning silence: conditional systems for RNA interference.Nat Methods. 2006 Sep;3(9):682-8. doi: 10.1038/nmeth914. Nat Methods. 2006. PMID: 16929312 Review.
-
Control of small inhibitory RNA levels and RNA interference by doxycycline induced activation of a minimal RNA polymerase III promoter.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Mar 6;34(5):e37. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl034. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16522642 Free PMC article.
-
Doxycycline regulated lentiviral vectors.Methods Mol Biol. 2010;614:69-76. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-533-0_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20225036
-
Lentiviral vector-mediated gene transfer and RNA silencing technology in neuronal dysfunctions.Mol Biotechnol. 2011 Feb;47(2):169-87. doi: 10.1007/s12033-010-9334-x. Mol Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 20862616 Review.
Cited by
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin regulates neutrophil extracellular trap formation via induction of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 α.Blood. 2012 Oct 11;120(15):3118-25. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-01-405993. Epub 2012 Aug 23. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22919032 Free PMC article.
-
Deregulation of the Hippo pathway in mouse mammary stem cells promotes mammary tumorigenesis.Mamm Genome. 2016 Dec;27(11-12):556-564. doi: 10.1007/s00335-016-9662-7. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Mamm Genome. 2016. PMID: 27601049 Free PMC article.
-
A lentiviral microRNA-based system for single-copy polymerase II-regulated RNA interference in mammalian cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Sep 13;102(37):13212-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506306102. Epub 2005 Sep 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16141338 Free PMC article.
-
RNA interference for antiviral therapy.J Gene Med. 2006 Aug;8(8):933-50. doi: 10.1002/jgm.929. J Gene Med. 2006. PMID: 16779870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Self-renewal of embryonic stem cells by a small molecule.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Nov 14;103(46):17266-71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608156103. Epub 2006 Nov 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17088537 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbas-Terki, T., W. Blanco-Bose, N. Deglon, W. Pralong, and P. Aebischer. 2002. Lentiviral-mediated RNA interference. Hum. Gene Ther. 13:2197-2201. - PubMed
-
- Brummelkamp, T. R., R. Bernards, and R. A. Agami. 2002. A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science 296:550-553. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

