Mechanisms of P/CAF auto-acetylation
- PMID: 12888487
- PMCID: PMC169960
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg655
Mechanisms of P/CAF auto-acetylation
Abstract
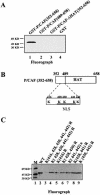
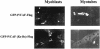
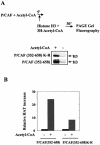
P/CAF is a histone acetyltransferase enzyme which was originally identified as a CBP/p300-binding protein. In this manuscript we report that human P/CAF is acetylated in vivo. We find that P/CAF is acetylated by itself and by p300 but not by CBP. P/CAF acetylation can be an intra- or intermolecular event. The intermolecular acetylation requires the N-terminal domain of P/CAF. The intramolecular acetylation targets five lysines (416-442) at the P/CAF C-terminus, which are in the nuclear localisation signal (NLS). Finally, we show that acetylation of P/CAF leads to an increment of its histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activity. These findings identify a new post-translation modification on P/CAF which may regulate its function.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Interaction of EVI1 with cAMP-responsive element-binding protein-binding protein (CBP) and p300/CBP-associated factor (P/CAF) results in reversible acetylation of EVI1 and in co-localization in nuclear speckles.J Biol Chem. 2001 Nov 30;276(48):44936-43. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M106733200. Epub 2001 Sep 21. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11568182
-
Transcription factor-dependent regulation of CBP and P/CAF histone acetyltransferase activity.EMBO J. 2001 Apr 17;20(8):1984-92. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.8.1984. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11296231 Free PMC article.
-
Acetylation-mediated transcriptional activation of the ETS protein ER81 by p300, P/CAF, and HER2/Neu.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Sep;23(17):6243-54. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.17.6243-6254.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12917345 Free PMC article.
-
Acetylation of general transcription factors by histone acetyltransferases.Curr Biol. 1997 Sep 1;7(9):689-92. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(06)00296-x. Curr Biol. 1997. PMID: 9285713 Review.
-
CBP and p300: HATs for different occasions.Biochem Pharmacol. 2004 Sep 15;68(6):1145-55. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2004.03.045. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15313412 Review.
Cited by
-
Acetylation of the response regulator RcsB controls transcription from a small RNA promoter.J Bacteriol. 2013 Sep;195(18):4174-86. doi: 10.1128/JB.00383-13. Epub 2013 Jul 12. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23852870 Free PMC article.
-
The acetyltransferase activity of the bacterial toxin YopJ of Yersinia is activated by eukaryotic host cell inositol hexakisphosphate.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jun 25;285(26):19927-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.126581. Epub 2010 Apr 29. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20430892 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolism, cytoskeleton and cellular signalling in the grip of protein Nepsilon - and O-acetylation.EMBO Rep. 2007 Jun;8(6):556-62. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400977. EMBO Rep. 2007. PMID: 17545996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autoacetylation of the histone acetyltransferase Rtt109.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 15;286(28):24694-701. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.251579. Epub 2011 May 23. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21606491 Free PMC article.
-
Biological processes and signal transduction pathways regulated by the protein methyltransferase SETD7 and their significance in cancer.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2018 Jul 13;3:19. doi: 10.1038/s41392-018-0017-6. eCollection 2018. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2018. PMID: 30013796 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Konberg R.D. and Lorch,Y. (1999) Chromatin-modifying and remodelling complexes. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 9, 148–151. - PubMed
-
- Kingston R.E. and Narlikar,G.J. (1999) ATP-dependent remodelling and acetylation as regulators of chromatin fluidity. Genes Dev., 13, 2339–2352. - PubMed
-
- Wu J. and Grunstein,M. (2000) 25 years after the nucleosome model: chromatin modifications. Trends Biochem. Sci., 25, 619–623. - PubMed
-
- Berger S. (2002) Histone modifications in transcriptional regulation. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 12, 142–148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

