The essential transcription factor Reb1p interacts with the CLB2 UAS outside of the G2/M control region
- PMID: 12888520
- PMCID: PMC169905
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg638
The essential transcription factor Reb1p interacts with the CLB2 UAS outside of the G2/M control region
Abstract
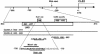
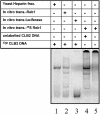
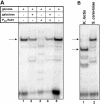
Regulation of CLB2 is important both for completion of the normal vegetative cell cycle in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and for departure from the vegetative cell cycle upon nitrogen deprivation. Cell cycle-regulated transcription of CLB2 in the G2/M phase is known to be brought about by a set of proteins including Mcm1p, Fkh2/1p and Ndd1p that associate with a 35 bp G2/M-specific sequence common to a set of co-regulated genes. CLB2 transcription is regulated by additional signals, including by nitrogen levels, by positive feedback from the Clb2-Cdc28 kinase, and by osmotic stress, but the corresponding regulatory sequences and proteins have not been identified. We have found that the essential Reb1 transcription factor binds with high affinity to a sequence upstream of CLB2, within a region implicated previously by others in regulated expression, but upstream of the known G2/M-specific site. CLB2 sequence from the region around the Reb1p site blocks activation by the Gal4 protein when positioned downstream of the Gal4-binding site. Since a mutation in the Reb1p site abrogates this effect, we suggest that Reb1p is likely to occupy this site in vivo.
Figures
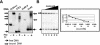

Similar articles
-
Forkhead transcription factors, Fkh1p and Fkh2p, collaborate with Mcm1p to control transcription required for M-phase.Curr Biol. 2000 Jul 27-Aug 10;10(15):896-906. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00618-7. Curr Biol. 2000. PMID: 10959837
-
Mcm1 is required to coordinate G2-specific transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Nov;15(11):5917-28. doi: 10.1128/MCB.15.11.5917. Mol Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 7565744 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle-regulated transcription of the CLB2 gene is dependent on Mcm1 and a ternary complex factor.Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;15(6):3129-37. doi: 10.1128/MCB.15.6.3129. Mol Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 7760809 Free PMC article.
-
The Isw2 chromatin-remodeling ATPase cooperates with the Fkh2 transcription factor to repress transcription of the B-type cyclin gene CLB2.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Apr;27(8):2848-60. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01798-06. Epub 2007 Feb 5. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17283050 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular determinants of the cell-cycle regulated Mcm1p-Fkh2p transcription factor complex.Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 May 1;31(9):2279-88. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg347. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12711672 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Promoter engineering with programmable upstream activating sequences in Aspergillus Niger cell factory.Microb Cell Fact. 2025 Jan 15;24(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12934-025-02642-y. Microb Cell Fact. 2025. PMID: 39815338 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic approach to detecting transcription factors in response to environmental stresses.BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 Dec 8;8:473. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-473. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 18067669 Free PMC article.
-
Condition-specific promoter activities in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Microb Cell Fact. 2018 Apr 10;17(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12934-018-0899-6. Microb Cell Fact. 2018. PMID: 29631591 Free PMC article.
-
The development and characterization of synthetic minimal yeast promoters.Nat Commun. 2015 Jul 17;6:7810. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8810. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26183606 Free PMC article.
-
RNAP-II molecules participate in the anchoring of the ORC to rDNA replication origins.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53405. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053405. Epub 2013 Jan 4. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23308214 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Surana U., Robitsch,H., Price,C., Schuster,T., Fitch,I., Futcher,A.B. and Nasmyth,K. (1991) The role of CDC28 and cyclins during mitosis in the budding yeast S.cerevisiae. Cell, 65, 145–161. - PubMed
-
- Richardson H., Lew,D.J., Henze,M., Sugimoto,K. and Reed,S.I. (1992) Cyclin-B homologs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae function in S phase and in G2. Genes Dev., 6, 2021–2034. - PubMed
-
- Nasmyth K. (1996) At the heart of the budding yeast cell cycle. Trends Genet., 12, 405–412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

