Identification of a G protein-coupled receptor for pheromone biosynthesis activating neuropeptide from pheromone glands of the moth Helicoverpa zea
- PMID: 12888624
- PMCID: PMC187832
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1632485100
Identification of a G protein-coupled receptor for pheromone biosynthesis activating neuropeptide from pheromone glands of the moth Helicoverpa zea
Abstract
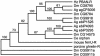
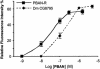
Pheromone biosynthesis-activating neuropeptide (PBAN), a peptide produced by the subesophageal ganglion, is used by a variety of moths to regulate pheromone production. PBAN acts directly on pheromone gland cells by using calcium and cAMP as second messengers. We have identified a gene encoding a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) from pheromone glands of the female moth Helicoverpa zea. The gene was identified based on sequence identity to a group of GPCRs from Drosophila that are homologous to neuromedin U receptors in vertebrates. The full-length PBAN receptor was subsequently cloned, expressed in Sf9 insect cells, and shown to mobilize calcium in response to PBAN. This response was dose-dependent (EC50 = 25 nM) with a maximum response at 300 nM and a minimal observable response at 10 nM. Four additional peptides produced by the PBAN-encoding gene were also tested for activity, and it was determined that three had similar activity to PBAN and the other was slightly less active. Peptides belonging to the same family as PBAN, namely pyrokinins, as well as the vertebrate neuromedin U peptide also induced a calcium response. We have identified a GPCR for the PBAN/pyrokinin family of peptides with a known function of stimulating pheromone biosynthesis in female moths. It is related to several receptors from insects (Drosophila and Anopheles) and to neuromedin U and ghrelin receptors from vertebrates.
Figures
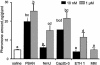


Similar articles
-
Structural and functional differences between pheromonotropic and melanotropic PK/PBAN receptors.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Nov;1830(11):5036-48. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.06.041. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23850474
-
Spatial distribution and differential expression of the PBAN receptor in tissues of adult Helicoverpa spp. (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae).Insect Mol Biol. 2007 Jun;16(3):287-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2583.2007.00725.x. Epub 2007 Feb 28. Insect Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17328713
-
Pheromone biosynthesis activating neuropeptide (PBAN): regulatory role and mode of action.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2009 May 15;162(1):69-78. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2008.04.004. Epub 2008 Apr 18. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 18495120 Review.
-
Molecular characterization of pheromone biosynthesis activating neuropeptide from the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (L.).Peptides. 2005 Dec;26(12):2404-11. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2005.04.016. Epub 2005 Jul 6. Peptides. 2005. PMID: 16005110
-
Regulation of pheromone biosynthesis in moths.Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2017 Dec;24:29-35. doi: 10.1016/j.cois.2017.09.002. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2017. PMID: 29208220 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of putative Type-I sex pheromone biosynthesis-related genes expressed in the female pheromone gland of Streltzoviella insularis.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 16;15(1):e0227666. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227666. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31945099 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Analysis of Ostrinia furnacalis Female Pheromone Gland: Esters Biosynthesis and Requirement for Mating Success.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Sep 17;12:736906. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.736906. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34603212 Free PMC article.
-
A novel physiological function of pheromone biosynthesis-activating neuropeptide in production of aggregation pheromone.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 5;13(1):5551. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-32833-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37019976 Free PMC article.
-
More than two decades of research on insect neuropeptide GPCRs: an overview.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2012 Nov 30;3:151. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2012.00151. eCollection 2012. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2012. PMID: 23226142 Free PMC article.
-
GPCR-Based Bioactive Peptide Screening Using Phage-Displayed Peptides and an Insect Cell System for Insecticide Discovery.Biomolecules. 2021 Apr 16;11(4):583. doi: 10.3390/biom11040583. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33923387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raina, A. K. & Klun, J. A. (1984) Science 225, 531–533. - PubMed
-
- Rafaeli, A. (2002) Int. Rev. Cytol. 213, 49–91. - PubMed
-
- Raina, A. K., Jaffe, H., Kempe, T. G., Keim, P., Blacher, R. W., Fales, H. M., Riley, C. T., Klun, J. A., Ridgway, R. L. & Hayes, D. K. (1989) Science 244, 796–798. - PubMed
-
- Raina, A. & Kempe, T. (1990) Insect Biochem. 20, 849–851.
-
- Ma, P. W. K., Roelofs, W. L. & Jurenka, R. A. (1996) J. Insect Physiol. 42, 257–266.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

