Suppressor of cytokine signalling gene expression is elevated in breast carcinoma
- PMID: 12888825
- PMCID: PMC2394374
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601115
Suppressor of cytokine signalling gene expression is elevated in breast carcinoma
Abstract
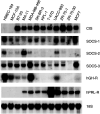
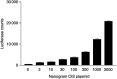
Cytokines are important for breast cell function, both as trophic hormones and as mediators of host defense mechanisms against breast cancer. Recently, inducible feedback suppressors of cytokine signalling (SOCS/JAB/SSI) have been identified, which decrease cell sensitivity to cytokines. We examined the expression of SOCS genes in 17 breast carcinomas and 10 breast cancer lines, in comparison with normal tissue and breast lines. We report elevated expression of SOCS-1-3 and CIS immunoreactive proteins within in situ ductal carcinomas and infiltrating ductal carcinomas relative to normal breast tissue. Significantly increased expression of SOCS-1-3 and CIS transcripts was also shown by quantitative in situ hybridisation within both tumour tissue and reactive stroma. CIS transcript expression was elevated in all 10 cancer lines, but not in control lines. However, there was no consistent elevation of other SOCS transcripts. CIS protein was shown by immunoblot to be present in all cancer lines at increased levels, mainly as the 47 kDa ubiquitinylated form. A potential proliferative role for CIS overexpression is supported by reports that CIS activates ERK kinases, and by strong induction in transient reporter assays with an ERK-responsive promoter. The in vivo elevation of SOCS gene expression may be part of the host/tumour response or a response to autocrine/paracrine GH and prolactin. However, increased CIS expression in breast cancer lines appears to be a specific lesion, and could simultaneously shut down STAT 5 signalling by trophic hormones, confer resistance to host cytokines and increase proliferation through ERK kinases.
Figures
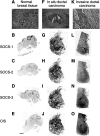
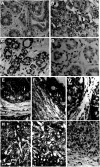
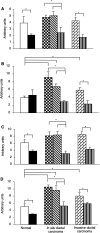
 ), cancerous ducts; (
), cancerous ducts; ( ), reactive stroma; (
), reactive stroma; ( ), invasive area; (
), invasive area; ( ), adjacent normal connective tissue; expressed in arbitrary units±s.e.m. *P<0.05.
), adjacent normal connective tissue; expressed in arbitrary units±s.e.m. *P<0.05.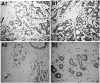
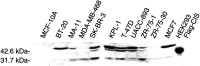

Similar articles
-
Growth hormone down-regulation of Interleukin-1beta and Interleukin-6 induced acute phase protein gene expression is associated with increased gene expression of suppressor of cytokine signal-3.Shock. 2003 Apr;19(4):314-20. doi: 10.1097/00024382-200304000-00004. Shock. 2003. PMID: 12688541
-
Suppressors of cytokine signalling: SOCS.APMIS. 2002 Dec;110(12):833-44. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0463.2002.1101201.x. APMIS. 2002. PMID: 12645661 Review.
-
Inhibition and restoration of prolactin signal transduction by suppressors of cytokine signaling.J Biol Chem. 1999 Aug 27;274(35):24497-502. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.35.24497. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10455112
-
Induction of JAB/SOCS-1/SSI-1 and CIS3/SOCS-3/SSI-3 is involved in gp130 resistance in cardiovascular system in rat treated with cardiotrophin-1 in vivo.Circ Res. 2001 Apr 13;88(7):727-32. doi: 10.1161/hh0701.088512. Circ Res. 2001. PMID: 11304496
-
SOCS: suppressors of cytokine signalling.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1998 Oct;30(10):1081-5. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(98)00067-3. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9785473 Review.
Cited by
-
STAT 5a expression in various lesions of the breast.Virchows Arch. 2006 Feb;448(2):165-71. doi: 10.1007/s00428-005-0056-6. Epub 2005 Aug 19. Virchows Arch. 2006. PMID: 16133357
-
RACK1 and CIS mediate the degradation of BimEL in cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jun 13;283(24):16416-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M802360200. Epub 2008 Apr 17. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18420585 Free PMC article.
-
Histone H1 and Chromosomal Protein HMGN2 Regulate Prolactin-induced STAT5 Transcription Factor Recruitment and Function in Breast Cancer Cells.J Biol Chem. 2017 Feb 10;292(6):2237-2254. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.764233. Epub 2016 Dec 29. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28035005 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of SOCS-Mediated Negative Feedback of Cytokine Signaling in Carcinogenesis and Its Significance in Cancer Treatment.Front Immunol. 2017 Feb 8;8:70. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00070. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28228755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) genes are downregulated in breast cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2018 Nov 19;16(1):226. doi: 10.1186/s12957-018-1529-9. World J Surg Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30453988 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams TE, Hansen JA, Starr R, Nicola NA, Hilton DJ, Billestrup NJ (1998) Growth hormone preferentially induces the rapid, transient expression of SOCS-3, a novel inhibitor of cytokine receptor signaling. J Biol Chem 273: 1285–1287 - PubMed
-
- Allione A, Consalvo M, Nani P, Lollini PL, Cavallo F, Giovarelli M, Forni M, Gulino A, Colombo MP, Dellabona P (1994) Immunizing and curative potential of replicating and non-replicating murine mammary adenocarcinoma cells engineered with interleukins -2, -4, -6, -7, -10, tumor necrosis factor α, GMCSF and γ interferon gene or admixed with conventional adjuvants. Cancer Res 54: 6022–6026 - PubMed
-
- Argetsinger LS, Carter-Su C (1996) Mechanism of signaling by GH receptor. Physiol Rev 4: 1089–1107 - PubMed
-
- Boutin JM, Edery M, Shirota M, Jolicoeur C, Lesueur L, Ali S, Gould D, Djiane J, Kelly PA (1989) Identification of a cDNA encoding a long form of prolactin receptor in human hepatoma and breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol 3: 1455–1461 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

