Molecular mechanisms underlying the interaction between ZD1839 ('Iressa') and cisplatin/5-fluorouracil
- PMID: 12888834
- PMCID: PMC2394392
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601131
Molecular mechanisms underlying the interaction between ZD1839 ('Iressa') and cisplatin/5-fluorouracil
Abstract
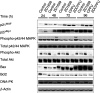
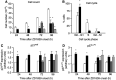
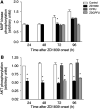
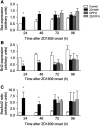
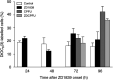
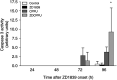
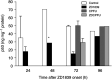
ZD1839 ('Iressa'), an orally active, selective epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is currently being investigated in clinical trials as a treatment for cancer. 'Iressa' is a trademark of the AstraZeneca group of companies. We have previously demonstrated a synergistic interaction between ZD1839 and cisplatin/5-fluorouracil (5FU) in CAL33, a human head and neck cancer cell line that markedly expresses EGFR. This study examined the effects of this drug combination on the cell cycle, cell cycle regulators, apoptosis-related factors, EGFR-related signalling and DNA repair in CAL33 cells. The cells were incubated with ZD1839 alone for 48 h, then cisplatin and 5FU were added. Exposure to the drug combination continued for a further 48 h. ZD1839 alone induced accumulation of cells in the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle at 24 h accompanied by a concomitant increase in p21, p27 and Bax, a significant decrease in Bcl2 and a decrease in Akt phosphorylation. A decrease in DNA-PK was observed at 48 h. ZD1839 alone had no effect on caspase-3 activity, but addition of ZD1839 to cisplatin-5FU led to a significant increase in caspase-3 activity at 96 h. Thus, ZD1839 affects key cellular pathways controlling cell proliferation, apoptosis and DNA repair. These data provide a rationale to support clinical trials combining ZD1839 and cisplatin-5FU and other protocols that combine EGFR-targeting agents with chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
Figures


References
-
- Backus HH, Dukers DF, van Groeningen CJ, Vos W, Bloemena E, Wouters D, van Riel JM, Smid K, Giaccone G, Pinedo HM, Peters GJ (2001) 5-Fluorouracil induced Fas upregulation associated with apoptosis in liver metastasis of colorectal cancer patients. Ann Oncol 12: 209–216 - PubMed
-
- Bancroft CC, Chen Z, Yeh J, Sunwoo JB, Yeh NT, Jackson S, Jackson C, Van Waes C (2002) Effects of pharmacologic antagonists of epidermal growth factor receptor, PI3 K and MEK signal kinases on NF-kappaB and AP-1 activation and IL-8 and VEGF expression in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma lines. Int J Cancer 99: 538–548 - PubMed
-
- Baselga J (2001) The EGFR as a target for anticancer therapy – focus on cetuximab. Eur J Cancer 37 (Suppl 4): S16–S22 - PubMed
-
- Baselga J, Norton L, Masui H, Pandiella A, Coplan K, Miller Jr WH, Mendelson J (1993) Antitumor effects of doxorubicin in combination with anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibodies. J Natl Cancer Inst 85: 1327–1333 - PubMed
-
- Bianco C, Bianco R, Tortora G, Damiano V, Guerrieri P, Montemaggi P, Mendelsohn J, De Placido S, Bianco AR, Ciardiello F (2000) Antitumor activity of combined treatment of human cancer cells with ionizing radiation and anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody C225 plus type I protein kinase A antisense oligonucleotide. Clin Cancer Res 6: 4343–4350 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

