Global screening for human viral pathogens
- PMID: 12890315
- PMCID: PMC3023425
- DOI: 10.3201/eid0907.030004
Global screening for human viral pathogens
Abstract
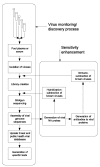
We propose a system for continuing surveillance of viral pathogens circulating in large human populations. We base this system on the physical isolation of viruses from large pooled samples of human serum and plasma (e.g., discarded specimens from diagnostic laboratories), followed by shotgun sequencing of the resulting genomes. The technology for concentrating virions from 100-L volumes was developed previously at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, and the means for purifying and concentrating virions from volumes in microliters have been developed recently. At the same time, marine virologists have developed efficient methods for concentrating, amplifying, and sequencing complex viral mixtures obtained from the ocean. Given this existing technology base, we believe an integrated, automated, and contained system for surveillance of the human "virome" can be implemented within 1 to 2 years. Such a system could monitor the levels of known viruses in human populations, rapidly detect outbreaks, and systematically discover novel or variant human viruses.
Figures
References
-
- Rohwer F, Seguritan V, Choi DH, Segall AM, Azam F. Production of shotgun libraries using random amplification. Biotechniques. 2001;31:108–17. - PubMed
-
- Steward GF, Montiel JL, Azam F. Genome size distributions indicate variability and similarities among marine viral assemblages from diverse environments. Limnol Oceanogr. 2000;45:1697–706. 10.4319/lo.2000.45.8.1697 - DOI
-
- Anderson NG, ed. The development of zonal centrifuges and ancillary systems for tissue fractionation and analysis. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966;21:526.
-
- Anderson NG, Harris WW, Barber AA, Rankin CT, Candler EL. Separation of sub-cellular components and viruses by combined rate- and isopycnic-zonal centrifugation. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966;21:253–83. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
