Post-training intra-basolateral amygdala infusions of norepinephrine enhance consolidation of memory for contextual fear conditioning
- PMID: 12890768
- PMCID: PMC6740722
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-17-06754.2003
Post-training intra-basolateral amygdala infusions of norepinephrine enhance consolidation of memory for contextual fear conditioning
Abstract
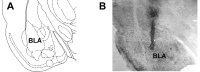
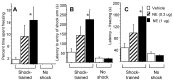
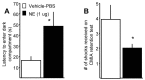
Post-training infusions of drugs, including noradrenergic agonists and antagonists, into the basolateral amygdala (BLA) influence the consolidation of memory for training in several tasks, including inhibitory avoidance. There is, however, conflicting evidence concerning whether post-training intra-BLA drug infusions modulate the consolidation of contextual fear conditioning (CFC). In the present study, norepinephrine (NE) was infused bilaterally into the BLA of male Sprague Dawley rats immediately after training on two CFC tasks: a Y-maze and a straight alley. Post-training intra-BLA infusions enhanced memory of CFC training in the Y-maze, as assessed by percentage of time spent freezing and shock arm entrance latencies. Post-training intra-BLA infusions of NE enhanced 48 hr retention of CFC training in the straight alley, as assessed by shock compartment entrance latencies and the number of shocks required to learn to avoid entering the shock compartment. These findings indicate that the consolidation of memory for CFC, like that for inhibitory avoidance training, is influenced by post-training neuromodulatory influences within the BLA. Thus, the findings provide additional evidence consistent with the hypothesis that the BLA has a general role in modulating memory consolidation.
Figures
References
-
- Brioni JD, Nagahara AH, McGaugh JL ( 1989) Involvement of the amygdala GABAergic system in the modulation of memory storage. Brain Res 487: 105-112. - PubMed
-
- Bucherelli C, Tassoni G, Bures J ( 1992) Time-dependent disruption of passive avoidance acquisition by post-training intra-amygdala injection of tetrodotoxin in rats. Neurosci Lett 140: 213-234. - PubMed
-
- Cangioli I, Baldi E, Mannaioni PF, Bucherelli C, Blandina P, Passani MB ( 2002) Activation of histaminergic H3 receptors in the rat basolateral amygdala improves expression of fear memory and enhances acetylcholine release. Eur J Neurosci 16: 521-528. - PubMed
-
- Ferry B, McGaugh JL ( 1999) Clenbuterol administration into the basolateral amygdala post training enhances retention in an inhibitory avoidance task. Neurobiol Learn Mem 72: 8-12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
