App gene dosage modulates endosomal abnormalities of Alzheimer's disease in a segmental trisomy 16 mouse model of down syndrome
- PMID: 12890772
- PMCID: PMC6740714
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-17-06788.2003
App gene dosage modulates endosomal abnormalities of Alzheimer's disease in a segmental trisomy 16 mouse model of down syndrome
Abstract
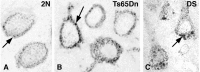
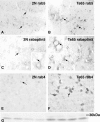
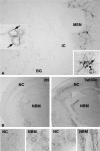
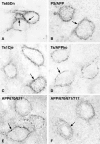
Altered neuronal endocytosis is the earliest known pathology in sporadic Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Down syndrome (DS) brain and has been linked to increased Abeta production. Here, we show that a genetic model of DS (trisomy 21), the segmental trisomy 16 mouse Ts65Dn, develops enlarged neuronal early endosomes, increased immunoreactivity for markers of endosome fusion (rab5, early endosomal antigen 1, and rabaptin5), and endosome recycling (rab4) similar to those in AD and DS individuals. These abnormalities are most prominent in neurons of the basal forebrain, which later develop aging-related atrophy and degenerative changes, as in AD and DS. We also show that App, one of the triplicated genes in Ts65Dn mice and human DS, is critical to the development of these endocytic abnormalities. Selectively deleting one copy of App or a small portion of the chromosome 16 segment containing App from Ts65Dn mice eliminated the endosomal phenotype. Overexpressing App at high levels in mice did not alter early endosomes, implying that one or more additional genes on the triplicated segment of chromosome 16 are also required for the Ts65Dn endosomal phenotype. These results identify an essential role for App gene triplication in causing AD-related endosomal abnormalities and further establish the pathogenic significance of endosomal dysfunction in AD.
Figures
References
-
- Allore R, O'Hanlon D, Price R, Neilson K, Willard HF, Cox DR, Marks A, Dunn RJ ( 1988) Gene encoding the beta subunit of S100 protein is on chromosome 21: implications for Down syndrome. Science 239: 1311-1313. - PubMed
-
- Bucci C, Parton RG, Mather IH, Stunnenberg H, Simons K, Hoflack B, Zerial M ( 1992) The small GTPase rab5 functions as a regulatory factor in the early endocytic pathway. Cell 70: 715-728. - PubMed
-
- Busciglio J, Yankner BA ( 1995) Apoptosis and increased generation of reactive oxygen species in Down's syndrome neurons in vitro Nature 378: 776-779. - PubMed
-
- Cataldo AM, Peterhoff CM, Troncoso JC, Gomez-Isla T, Hyman BT, Nixon RA ( 2000a) Endocytic pathway abnormalities precede amyloid beta deposition in sporadic Alzheimer's disease and Down syndrome: differential effects of APOE genotype and presenilin mutations. Am J Pathol 157: 277-286. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
