N-type calcium channel alpha1B subunit (Cav2.2) knock-out mice display hyperactivity and vigilance state differences
- PMID: 12890773
- PMCID: PMC6740709
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-17-06793.2003
N-type calcium channel alpha1B subunit (Cav2.2) knock-out mice display hyperactivity and vigilance state differences
Abstract
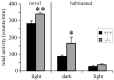
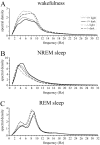
Differential properties of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels have been primarily ascribed to the alpha1 subunit, of which 10 different subtypes are currently known. For example, channels that conduct the N-type Ca2+ current possess the alpha1B subunit (Cav2.2), which has been localized, inter alia, to the piriform cortex, hippocampus, hypothalamus, locus coeruleus, dorsal raphe, thalamic nuclei, and granular layer of the cortex. Some of these regions have been previously implicated in metabolic and vigilance state control, and selective block of the N-type Ca2+ channel causes circadian rhythm disruption. In this study of Cav2.2-/- knock-out mice, we examined potential differences in feeding behavior, spontaneous locomotion, and the sleep-wake cycle. Cav2.2-/- mice did not display an overt metabolic phenotype but were hyperactive, demonstrating a 20% increase in activity under novel conditions and a 95% increase in activity under habituated conditions during the dark phase, compared with wild-type littermates. Cav2.2-/- mice also displayed vigilance state differences during the light phase, including increased consolidation of rapid-eye movement (REM) sleep and increased intervals between non-REM (NREM) and wakefulness episodes. EEG spectral power was increased during wakefulness and REM sleep and was decreased during NREM sleep in Cav2.2-/- mice. These results indicate a role of the N-type Ca2+ channel in activity and vigilance state control, which we interpret in terms of effects on neurotransmitter release.
Figures
References
-
- Bayliss DA, Li YW, Talley EM ( 1997) Effects of serotonin on caudal raphe neurons: inhibition of N- and P/Q-type calcium channels and the after-hyperpolarization. J Neurophysiol 77: 1362-1374. - PubMed
-
- Brazhnik ES, Vinogradova OS ( 1986) Control of the neuronal rhythmic bursts in the septal pacemaker of theta-rhythm: effects of anaesthetic and anticholinergic drugs. Brain Res 380: 94-106. - PubMed
-
- Catterall WA ( 1998) Structure and function of neuronal Ca2+ channels and their role in neurotransmitter release. Cell Calcium 24: 307-323. - PubMed
-
- Chemelli RM, Willie JT, Sinton CM, Elmquist JK, Scammell T, Lee C, Richardson JA, Williams SC, Xiong Y, Kisanuki Y, Fitch TE, Nakazato M, Hammer RE, Saper CB, Yanagisawa M ( 1999) Narcolepsy in orexin knockout mice: molecular genetics of sleep regulation. Cell 98: 437-451. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
