Evidence for chelatable zinc in the extracellular space of the hippocampus, but little evidence for synaptic release of Zn
- PMID: 12890779
- PMCID: PMC6740710
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-17-06847.2003
Evidence for chelatable zinc in the extracellular space of the hippocampus, but little evidence for synaptic release of Zn
Erratum in
- J Neurosci. 2004 Jan 21;24(3):Table of Contents
Abstract
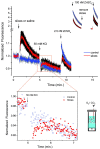
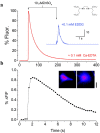
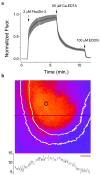
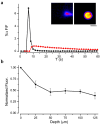
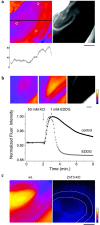
Zinc colocalizes with glutamate in the synaptic vesicles of certain glutamatergic vesicles in the mammalian brain. Here, I introduce a method for detecting Zn in the extracellular space of brain slices and another method for detecting the passage of Zn out of the slice. In both cases, the fluorimetric Zn probe FluoZin-3 is used in conjunction with a slow Zn chelator, Ca-EDTA, to reduce background fluorescence. In addition, a new Zn chelator, ethylenediiminodi-2-pentanedioic acid, with little affinity for Ca or Mg is introduced. These tools are then used to show that little Zn (approximately 2 nm) is released during the course of synaptic transmission into the extracellular space. However, when hippocampal slices are subjected to a high potassium stimulus (50 mM) combined with an increase in osmolarity, Zn is externalized in the Timm's-stained areas (approximately 6 nm). This stimulus also leads to even greater Zn elevations in area CA1 that is only weakly stained by the Timm's method. Nevertheless, even under these conditions, little if any Zn makes its way out of the slices. I present evidence for a layer of Zn in the extracellular space that maps onto the Timm's stained region of the hippocampus. This Zn veneer appears to be loosely associated with molecules in the extracellular space and may be the raison d'être for vesicular Zn.
Figures

References
-
- Anikstejn L, Charton G, Ben-Ari Y ( 1987) Selective release of endogenous zinc from the hippocampal mossy fibers in situ. Brain Res 404: 58-64. - PubMed
-
- Arslan P, Di Virgilio F, Beltrame M, Tsien RY, Pozzan T ( 1985) Cytosolic Ca2+ homeostasis in Ehrlich and Yoshida carcinomas: a new, membrane-permeant chelator of heavy metals reveals that these ascites tumor cell lines have normal cytosolic free Ca2+ J Biol Sci 260: 2719-2727. - PubMed
-
- Assaf SY, Chung S-H ( 1984) Release of endogenous Zn2+ from brain tissue during activity. Nature 308: 734-735. - PubMed
-
- Billington N, Knight AW ( 2001) Seeing the wood through the trees: a review of techniques for distinguishing green fluorescent protein from endogenous autofluorescence. Anal Biochem 291: 175-197. - PubMed
-
- Budde T, Minta A, White JA, Kay AR ( 1997) Imaging free zinc in synaptic terminals in live hippocampal slices. Neuroscience 79: 347-358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
