Development and subunit composition of synaptic NMDA receptors in the amygdala: NR2B synapses in the adult central amygdala
- PMID: 12890782
- PMCID: PMC6740716
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-17-06876.2003
Development and subunit composition of synaptic NMDA receptors in the amygdala: NR2B synapses in the adult central amygdala
Abstract
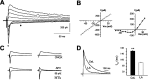
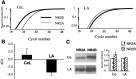
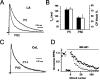
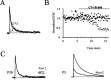
NMDA receptors are well known to play an important role in synaptic development and plasticity. Functional NMDA receptors are heteromultimers thought to contain two NR1 subunits and two or three NR2 subunits. In central neurons, NMDA receptors at immature glutamatergic synapses contain NR2B subunits and are largely replaced by NR2A subunits with development. At mature synapses, NMDA receptors are thought to be multimers that contain either NR1/NR2A or NR1/NR2A/NR2B subunits, whereas receptors that contain only NR1/NR2B subunits are extrasynaptic. Here, we have studied the properties of NMDA receptors at glutamatergic synapses in the lateral and central amygdala. We find that NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic currents in the central amygdala in both immature and mature synapses have slow kinetics and are substantially blocked by the NR2B-selective antagonists (1S, 2S)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-(4-hydroxy-4-phenylpiperidino)-1-propano and ifenprodil, indicating that there is no developmental change in subunit composition. In contrast, at synapses on pyramidal neurons in the lateral amygdala, whereas NMDA EPSCs at immature synapses are slow and blocked by NR2B-selective antagonists, at mature synapses their kinetics are faster and markedly less sensitive to NR2B-selective antagonists, consistent with a change from NR2B to NR2A subunits. Using real-time PCR and Western blotting, we show that in adults the ratio of levels of NR2B to NR2A subunits is greater in the central amygdala than in the lateral amygdala. These results show that the subunit composition synaptic NMDA receptors in the lateral and central amygdala undergo distinct developmental changes.
Figures


References
-
- Behe P, Stern P, Wyllie DJ, Nassar M, Schoepfer R, Colquhoun D ( 1995) Determination of NMDA NR1 subunit copy number in recombinant NMDA receptors. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 262: 205-213. - PubMed
-
- Blair HT, Schafe GE, Bauer EP, Rodrigues SM, LeDoux JE ( 2001) Synaptic plasticity in the lateral amygdala: a cellular hypothesis of fear conditioning. Learn Mem 8: 229-242. - PubMed
-
- Carmignoto G, Vicini S ( 1992) Activity-dependent decrease in NMDA receptor responses during development of the visual cortex. Science 258: 1007-1011. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
