Unconjugated bilirubin in human bile: the nucleating factor in cholesterol cholelithiasis?
- PMID: 12890809
- PMCID: PMC1770027
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.56.8.596
Unconjugated bilirubin in human bile: the nucleating factor in cholesterol cholelithiasis?
Abstract
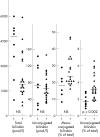
Aims: To investigate the concentrations of bilirubin, bilirubin conjugates, phospholipid, and cholesterol in the gall bladder bile obtained at surgery from patients with and without cholesterol gallstones.
Methods: Gall bladder bile was collected during surgery, by puncture, from 20 patients with gallstones undergoing routine cholecystectomy and from eight patients with normal liver blood tests. Concentrations of bilirubin, bilirubin conjugates, phospholipid, and cholesterol were measured using standard procedures.
Results: The proportion of total bilirubin that was unconjugated was significantly higher in the bile from patients with stones than in bile from control patients, whether or not the bile from either group was saturated with cholesterol or not. Indeed, the mean concentration of cholesterol was significantly higher in control bile samples.
Conclusion: The presence of stones was more closely related to the proportion of unconjugated bilirubin than to the degree of saturation of bile with cholesterol. Bilirubin and its metabolites probably play an important part in the formation of cholesterol gallstones.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intermittent secretion of abnormal bile in patients with cholesterol gall stones.Br Med J. 1972 Nov 4;4(5835):263-6. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5835.263. Br Med J. 1972. PMID: 5083887 Free PMC article.
-
Biliary lipid secretion in cholesterol gallstone disease. The effect of cholecystectomy and obesity.J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):828-40. doi: 10.1172/JCI108705. J Clin Invest. 1977. PMID: 856870 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleation of cholesterol monohydrate crystals from hepatic and gall-bladder bile of patients with cholesterol gall stones.Gut. 1983 Sep;24(9):836-44. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.9.836. Gut. 1983. PMID: 6884818 Free PMC article.
-
Unconjugated bilirubin and cholesterol gallstone formation.Hepatology. 1990 Sep;12(3 Pt 2):219S-224S; discussion 224S-226S. Hepatology. 1990. PMID: 2210652 Review.
-
Pigment gallstones.Gastroenterology. 1977 Jan;72(1):167-82. Gastroenterology. 1977. PMID: 318581 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitative assessment of the multiple processes responsible for bilirubin homeostasis in health and disease.Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2014 Sep 2;7:307-28. doi: 10.2147/CEG.S64283. eCollection 2014. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25214800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gallstones in chronic liver disease.J Gastrointest Surg. 2005 May-Jun;9(5):739-46. doi: 10.1016/j.gassur.2004.09.041. J Gastrointest Surg. 2005. PMID: 15862273 Review.
-
A product of heme catabolism modulates bacterial function and survival.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(7):e1003507. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003507. Epub 2013 Jul 25. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23935485 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction on the abundance of biliary microbiota (biliary microecology) in patients with common bile duct stones.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Dec 7;12:1001441. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1001441. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36569207 Free PMC article.
-
Obstructive-Type Jaundice without Bile Duct Dilatation in Generalized Peritonitis Is a Specific Sign of Spontaneous Gall Bladder Perforation.Case Rep Med. 2020 Sep 22;2020:6504260. doi: 10.1155/2020/6504260. eCollection 2020. Case Rep Med. 2020. PMID: 33061989 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abei M, Kawczak P, Nuutinen H, et al. Isolation and characterisation of a cholesterol crystallization promoter from human bile. Gastroenterology 1993;104:539–48. - PubMed
-
- Ohya T, Schwarzendrube J, Busch N, et al. Isolation of a human biliary glycoprotein inhibitor of cholesterol crystallization. Gastroenterology 1993;104:527–38. - PubMed
-
- Been JM, Bills PM, Lewis D. Microstructure of gallstones. Gastroenterology 1979;76:548–55. - PubMed
-
- Ostrow JD. Unconjugated bilirubin and cholesterol gallstone formation. Hepatology 1990;12:219S–26S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
