Unconjugated bilirubin in human bile: the nucleating factor in cholesterol cholelithiasis?
- PMID: 12890809
- PMCID: PMC1770027
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.56.8.596
Unconjugated bilirubin in human bile: the nucleating factor in cholesterol cholelithiasis?
Abstract
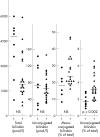
Aims: To investigate the concentrations of bilirubin, bilirubin conjugates, phospholipid, and cholesterol in the gall bladder bile obtained at surgery from patients with and without cholesterol gallstones.
Methods: Gall bladder bile was collected during surgery, by puncture, from 20 patients with gallstones undergoing routine cholecystectomy and from eight patients with normal liver blood tests. Concentrations of bilirubin, bilirubin conjugates, phospholipid, and cholesterol were measured using standard procedures.
Results: The proportion of total bilirubin that was unconjugated was significantly higher in the bile from patients with stones than in bile from control patients, whether or not the bile from either group was saturated with cholesterol or not. Indeed, the mean concentration of cholesterol was significantly higher in control bile samples.
Conclusion: The presence of stones was more closely related to the proportion of unconjugated bilirubin than to the degree of saturation of bile with cholesterol. Bilirubin and its metabolites probably play an important part in the formation of cholesterol gallstones.
Figures

References
-
- Abei M, Kawczak P, Nuutinen H, et al. Isolation and characterisation of a cholesterol crystallization promoter from human bile. Gastroenterology 1993;104:539–48. - PubMed
-
- Ohya T, Schwarzendrube J, Busch N, et al. Isolation of a human biliary glycoprotein inhibitor of cholesterol crystallization. Gastroenterology 1993;104:527–38. - PubMed
-
- Been JM, Bills PM, Lewis D. Microstructure of gallstones. Gastroenterology 1979;76:548–55. - PubMed
-
- Ostrow JD. Unconjugated bilirubin and cholesterol gallstone formation. Hepatology 1990;12:219S–26S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
