Measurement of 5-hydroxy-2-aminovaleric acid as a specific marker of metal catalysed oxidation of proline and arginine residues of low density lipoprotein apolipoprotein B-100 in human atherosclerotic lesions
- PMID: 12890816
- PMCID: PMC1770034
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.56.8.622
Measurement of 5-hydroxy-2-aminovaleric acid as a specific marker of metal catalysed oxidation of proline and arginine residues of low density lipoprotein apolipoprotein B-100 in human atherosclerotic lesions
Abstract
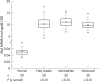
gamma-Glutamyl-semialdehyde (gammaGSA) is a major product of the metal catalysed oxidation of apolipoprotein B-100 (apoB-100) proline and arginine residues. On reduction, gammaGSA forms 5-hydroxy-2-aminovaleric acid (HAVA). This report describes the application of HAVA measurement to characterise the formation of gammaGSA in low density lipoprotein (LDL) recovered from human atherosclerotic lesions. HAVA concentrations were greatly increased in LDL from early (mean, 10.25; SD, 3.49 mol/mol apoB-100; p < 0.01), intermediate (mean, 11.18; SD, 2.37 mol/mol apoB-100; p < 0.01), and advanced (mean, 9.91; SD, 2.15 mol/mol apoB-100; p < 0.01) lesions, when compared with LDL from normal aortic tissue (mean, 0.05; SD, 0.01 mol/mol apoB-100). These findings support the hypothesis that pathways involving metal catalysed oxidation of LDL apoB-100 are of pathological importance in atherogenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Ross R. Atherosclerosis—an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med 1999;340:115–26. - PubMed
-
- Podrez EA, Abu-Soud HM, Hazen SL. Myeloperoxidase-generated oxidants and atherosclerosis. Free Radic Biol Med 2000;28:1717–25. - PubMed
-
- Miller YI, Shaklai N. Kinetics of hemin distribution in plasma reveals its role in lipoprotein oxidation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1999;1454:153–64. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous