Expression of BCR/ABL and BCL-2 in myeloid progenitors leads to myeloid leukemias
- PMID: 12890867
- PMCID: PMC187741
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1633833100
Expression of BCR/ABL and BCL-2 in myeloid progenitors leads to myeloid leukemias
Abstract
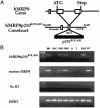
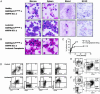
Chronic myelogenous leukemia is a myeloproliferative disorder (MPD) that, over time, progresses to acute leukemia. Both processes are closely associated with the t(9;22) chromosomal translocation that creates the BCR/ABL fusion gene in hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and their progeny. Chronic myelogenous leukemia is therefore classified as an HSC disorder in which a clone of multipotent HSCs is likely to be malignantly transformed, although direct evidence for malignant t(9;22)+ HSCs is lacking. To test whether HSC malignancy is required, we generated hMRP8p210BCR/ABL transgenic mice in which expression of BCR/ABL is absent in HSCs and targeted exclusively to myeloid progenitors and their myelomonocytic progeny. Four of 13 BCR/ABL transgenic founders developed a chronic MPD, but only one progressed to blast crisis. To address whether additional oncogenic events are required for progression to acute disease, we crossed hMRP8p210BCR/ABL mice to apoptosis-resistant hMRP8BCL-2 mice. Of 18 double-transgenic animals, 9 developed acute myeloid leukemias that were transplantable to wild-type recipients. Taken together, these data indicate that a MPD can arise in mice without expression of BCR/ABL in HSCs and that additional mutations inhibiting programmed cell death may be critical in the transition of this disease to blast-crisis leukemia.
Figures
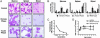
References
-
- Kalidas, M., Kantarjian, H. & Talpaz, M. (2001) J. Am. Med. Assoc. 286, 895–898. - PubMed
-
- Nowell, P. C. & Hungerford, D. A. (1960) Science 132, 1497–1501.
-
- Rowley, J. D. (1973) Nature 243, 290–293. - PubMed
-
- Groffen, J., Stephenson, J. R., Heisterkamp, N., de Klein, A., Bartram, C. R. & Grosveld, G. (1984) Cell 36, 93–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

