Roles of HNK-1 carbohydrate epitope and its synthetic glucuronyltransferase genes on migration of rat neural crest cells
- PMID: 12892407
- PMCID: PMC1571138
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1469-7580.2003.00205.x
Roles of HNK-1 carbohydrate epitope and its synthetic glucuronyltransferase genes on migration of rat neural crest cells
Abstract
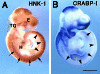
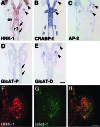
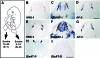
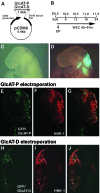
HNK-1 carbohydrate epitope is localized on the surface of avian neural crest cells (NCCs), and is necessary for their migration. However, it is still disputed whether the epitope works in similar ways in mammalian embryos. In this study, we found that HNK-1 carbohydrate epitope was specifically detected in some of the cranial ganglia, migrating trunk NCCs and some non-NCC derivatives in the rat embryo. Two genes encoding glucuronyltransferases that synthesize the HNK-1 epitope in vitro (GlcAT-P and GlcAT-D) were recently identified in the rat. Interestingly, the NCCs in the cranial ganglia expressed the GlcAT-D gene, whereas the migrating trunk NCCs expressed the GlcAT-P gene. To investigate in vivo functions of the GlcATs in the NCC migration further, we overexpressed GlcAT genes by electroporation in the cranial NCCs in cultured rat embryos. Transfection of both GlcAT genes resulted in efficient synthesis of the HNK-1 epitope in the NCCs. GlcAT-P overexpression increased distance of cranial NCC migration, whereas GlcAT-D overexpression did not show this effect. Our data suggest that the HNK-1 epitope synthesized by different GlcATs is involved in migration in the sublineages of the NCCs in the rat embryo, and that GlcAT-P and GlcAT-D mediate different effects on the NCC migration.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential expression of two glucuronyltransferases synthesizing HNK-1 carbohydrate epitope in the sublineages of the rat myogenic progenitors.Mech Dev. 2000 Nov;98(1-2):145-9. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(00)00449-4. Mech Dev. 2000. PMID: 11044619
-
Cloning and expression of a novel galactoside beta1, 3-glucuronyltransferase involved in the biosynthesis of HNK-1 epitope.J Biol Chem. 1999 Jun 11;274(24):17115-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.24.17115. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10358066
-
[Molecular biological approach to functions of telencephalin, a cell adhesion molecule and HNK-1 carbohydrate epitope, which is commonly expressed on cell adhesion molecules in the nervous system].Yakugaku Zasshi. 1998 Oct;118(10):431-46. doi: 10.1248/yakushi1947.118.10_431. Yakugaku Zasshi. 1998. PMID: 9800516 Review. Japanese.
-
cDNA cloning, genomic structure and chromosomal mapping of the mouse glucuronyltransferase-S involved in the biosynthesis of the HNK-1 carbohydrate epitope.Gene. 2002 Aug 21;296(1-2):29-36. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(02)00840-5. Gene. 2002. PMID: 12383500
-
[Roles of the HNK-1 carbohydrate epitope in the nervous system].Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001 Sep;21(3):95-9. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001. PMID: 11769463 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Spatiotemporal distribution of neural crest cells in the common wall lizard Podarcis muralis.Dev Dyn. 2025 Jun;254(6):551-567. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.758. Epub 2024 Nov 19. Dev Dyn. 2025. PMID: 39560189 Free PMC article.
-
Regenerative effects of human embryonic stem cell-derived neural crest cells for treatment of peripheral nerve injury.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018 Apr;12(4):e2099-e2109. doi: 10.1002/term.2642. Epub 2018 Feb 18. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018. PMID: 29327452 Free PMC article.
-
The Ocular Surface and the Anterior Segment of the Eye in the Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 10;26(2):532. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020532. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulated expression and neural functions of human natural killer-1 (HNK-1) carbohydrate.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Dec;69(24):4135-47. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1036-z. Epub 2012 Jun 6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22669261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of local and systemic treatment with human natural killer-1 mimetic peptide (HNK-1) after ventral root avulsion and reimplantation in mice.J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2024 May 20;30:e20230065. doi: 10.1590/1678-9199-JVATITD-2023-0065. eCollection 2024. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 38770186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abo T, Balch CM. A differentiation antigen of human NK and K cells identified by a monoclonal antibody (HNK-1) J. Immunol. 1981;127:1024–1029. - PubMed
-
- Aoyama N, Tamaki H, Kikawada R, Yamashina S. Development of the conduction system in the rat heart as determined by Leu-7 (HNK-1) immunohistochemistry and computer graphics reconstruction. Lab. Invest. 1995;72:355–366. - PubMed
-
- Ariga T, Kohriyama T, Freddo L, Latov N, Saito M, Kon K, et al. Characterization of sulfated glucuronic acid containing glycolipids reacting with IgM M-proteins in patients with neuropathy. J. Biol. Chem. 1987;262:848–853. - PubMed
-
- Bakker H, Friedmann I, Oka S, Kawasaki T, Nifant’ev N, Schachner M, et al. Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding a sulfotransferase involved in the biosynthesis of the HNK-1 carbohydrate epitope. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:29942–29946. - PubMed
-
- Bannerman PG, Oliver TM, Nichols WL, Jr, Xu Z. The spatial and temporal expression of HNK-1 by myogenic and skeletogenic cells in the embryonic rat. Cell Tissue Res. 1998;294:289–295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

