Exclusion of germ plasm proteins from somatic lineages by cullin-dependent degradation
- PMID: 12894212
- PMCID: PMC1892537
- DOI: 10.1038/nature01887
Exclusion of germ plasm proteins from somatic lineages by cullin-dependent degradation
Abstract
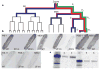
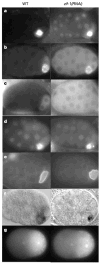
In many animals, establishment of the germ line depends on segregation of a specialized cytoplasm, or 'germ plasm', to a small number of germline precursor cells during early embryogenesis. Germ plasm asymmetry involves targeting of RNAs and proteins to a specific region of the oocyte and/or embryo. Here we demonstrate that germ plasm asymmetry also depends on degradation of germline proteins in non-germline (somatic) cells. We show that five CCCH finger proteins, components of the Caenorhabditis elegans germ plasm, are targeted for degradation by the novel CCCH-finger-binding protein ZIF-1. ZIF-1 is a SOCS-box protein that interacts with the E3 ubiquitin ligase subunit elongin C. Elongin C, the cullin CUL-2, the ring finger protein RBX-1 and the E2 ubiquitin conjugation enzyme UBC5 (also known as LET-70) are all required in vivo for CCCH finger protein degradation. Degradation is activated in somatic cells by the redundant CCCH finger proteins MEX-5 and MEX-6, which are counteracted in the germ line by the PAR-1 kinase. We propose that segregation of the germ plasm involves both stabilization of germline proteins in the germ line and cullin-dependent degradation in the soma.
Figures


References
-
- Houston DW, King ML. Germ plasm and molecular determinants of germ cell fate. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2000;50:155–181. - PubMed
-
- Kloc M, et al. RNA localization and germ cell determination in Xenopus. Int Rev Cytol. 2001;203:63–91. - PubMed
-
- Guedes S, Priess JR. The C. elegans MEX-1 protein is present in germline blastomeres and is a P granule component. Development. 1997;124:731–739. - PubMed
-
- Mello CC, et al. The PIE-1 protein and germline specification in C. elegans embryos. Nature. 1996;382:710–712. - PubMed
-
- Tabara H, Hill RJ, Mello CC, Priess JR, Kohara Y. pos-1 encodes a cytoplasmic zinc-finger protein essential for germline specification in C. elegans. Development. 1999;126:1–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

