CD95 ligand--death factor and costimulatory molecule?
- PMID: 12894217
- PMCID: PMC7091748
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401305
CD95 ligand--death factor and costimulatory molecule?
Abstract
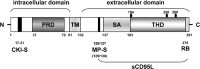
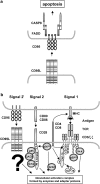
The CD95 ligand is involved as a death factor in the regulation of activation-induced cell death, establishment of immune privilege and tumor cell survival. In addition, CD95L may serve as a costimulatory molecule for T-cell activation. Alterations in expression or shedding of membrane and soluble CD95L are associated with numerous diseases, and underscore the pathophysiological relevance of the CD95/CD95L system. In most cases, the causal link between altered CD95L expression and pathophysiology is unknown. Given the potency of the molecule to regulate death and survival of many different cell types, the control of CD95L production, transport, storage, shedding and inactivation is of tremendous biological and clinical interest. This review summarizes the current knowledge, hypotheses and controversies about CD95L as a multifunctional ligand and receptor. It considers the different roles of membrane and soluble forms of CD95L and the complex networks of intracellular dynamics of protein trafficking, as well as the potential bidirectional signal transduction capacity of CD95L, with a focus on molecular interactions that have been worked out over the past years.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Slowly getting a clue on CD95 ligand biology.Biochem Pharmacol. 2003 Oct 15;66(8):1417-26. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(03)00492-1. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 14555216 Review.
-
Hyperosmolarity triggers CD95 membrane trafficking and sensitizes rat hepatocytes toward CD95L-induced apoptosis.Hepatology. 2002 Sep;36(3):602-14. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.35447. Hepatology. 2002. PMID: 12198652
-
Promotion of activated human B cell apoptosis and inhibition of Ig production by soluble CD95 ligand: CD95-based downregulation of Ig production need not culminate in activated B cell death.Cell Immunol. 2000 Jul 10;203(1):1-11. doi: 10.1006/cimm.2000.1675. Cell Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10915556
-
Function and regulation of the CD95 (APO-1/Fas) ligand in the immune system.Semin Immunol. 2003 Jun;15(3):145-57. doi: 10.1016/s1044-5323(03)00030-7. Semin Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14563113 Review.
-
Multiple interactions of the cytosolic polyproline region of the CD95 ligand: hints for the reverse signal transduction capacity of a death factor.FEBS Lett. 2001 Dec 7;509(2):255-62. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(01)03174-x. FEBS Lett. 2001. PMID: 11741599
Cited by
-
Adoptive transfer of splenocytes to study cell-mediated immune responses in hepatitis C infection using HCV transgenic mice.Comp Hepatol. 2010 Aug 20;9:7. doi: 10.1186/1476-5926-9-7. Comp Hepatol. 2010. PMID: 20727132 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Bcl-2 family proteins and caspases in the regulation of apoptosis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2011 May;351(1-2):41-58. doi: 10.1007/s11010-010-0709-x. Epub 2011 Jan 6. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21210296 Review.
-
Palmitoylation of human FasL modulates its cell death-inducing function.Cell Death Dis. 2010 Oct 21;1(10):e88. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2010.62. Cell Death Dis. 2010. PMID: 21368861 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane trafficking of death receptors: implications on signalling.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Jul 11;14(7):14475-503. doi: 10.3390/ijms140714475. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23852022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Death receptors and caspases: role in lymphocyte proliferation, cell death, and autoimmunity.Immunol Res. 2005;33(2):149-66. doi: 10.1385/IR:33:2:149. Immunol Res. 2005. PMID: 16234581 Review.
References
-
- Eischen CM, Schilling JD, Lynch DH, Krammer PH, Leibson PJ. Fc receptor-induced expression of Fas ligand on activated NK cells facilitates cell-mediated cytotoxicity and subsequent autocrine NK cell apoptosis. J. Immunol. 1996;156:2693–2699. - PubMed
-
- Kiener PA, Davis PM, Rankin BM, Klebanoff SJ, Ledbetter JA, Starling GC, Liles WC. Human monocytic cells contain high levels of intracellular Fas ligand: rapid release following cellular activation. J. Immunol. 1997;159:1594–1598. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

