The virulence activator AphA links quorum sensing to pathogenesis and physiology in Vibrio cholerae by repressing the expression of a penicillin amidase gene on the small chromosome
- PMID: 12897002
- PMCID: PMC166470
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.16.4825-4836.2003
The virulence activator AphA links quorum sensing to pathogenesis and physiology in Vibrio cholerae by repressing the expression of a penicillin amidase gene on the small chromosome
Abstract
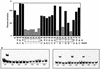
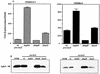
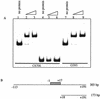
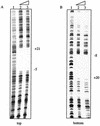
Activation of the tcpPH promoter on the Vibrio pathogenicity island by AphA and AphB initiates the Vibrio cholerae virulence cascade and is regulated by quorum sensing through the repressive action of HapR on aphA expression. To further understand how the chromosomally encoded AphA protein activates tcpPH expression, site-directed mutagenesis was used to identify the base pairs critical for AphA binding and transcriptional activation. This analysis revealed a region of partial dyad symmetry, TATGCA-N6-TNCNNA, that is important for both of these activities. Searching the V. cholerae genome for this binding site permitted the identification of a second one upstream of a penicillin V amidase (PVA) gene on the small chromosome. AphA binds to and footprints this site, which overlaps the pva transcriptional start, consistent with its role as a repressor at this promoter. Since aphA expression is under quorum-sensing control, the response regulators LuxO and HapR also influence pva expression. Thus, pva is repressed at low cell density when AphA levels are high, and it is derepressed at high cell density when AphA levels are reduced. Penicillin amidases are thought to function as scavengers for phenylacetylated compounds in the nonparasitic environment. That AphA oppositely regulates the expression of pva from that of virulence, together with the observation that PVA does not play a role in virulence, suggests that these activities are coordinated to serve V. cholerae in different biological niches.
Figures

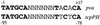
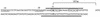
Similar articles
-
Overlapping binding sites for the virulence gene regulators AphA, AphB and cAMP-CRP at the Vibrio cholerae tcpPH promoter.Mol Microbiol. 2001 Jul;41(2):393-407. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02518.x. Mol Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11489126
-
Regulation of virulence gene expression in Vibrio cholerae by quorum sensing: HapR functions at the aphA promoter.Mol Microbiol. 2002 Nov;46(4):1135-47. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03229.x. Mol Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12421317
-
Vibrio cholerae AphA uses a novel mechanism for virulence gene activation that involves interaction with the LysR-type regulator AphB at the tcpPH promoter.Mol Microbiol. 2004 Jul;53(1):129-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04121.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15225309
-
The quorum sensing regulator HapR downregulates the expression of the virulence gene transcription factor AphA in Vibrio cholerae by antagonizing Lrp- and VpsR-mediated activation.Mol Microbiol. 2007 May;64(4):953-67. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05693.x. Mol Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17501920
-
Regulation of virulence in Vibrio cholerae.Int J Med Microbiol. 2001 May;291(2):81-8. doi: 10.1078/1438-4221-00104. Int J Med Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11437342 Review.
Cited by
-
The virulence transcriptional activator AphA enhances biofilm formation by Vibrio cholerae by activating expression of the biofilm regulator VpsT.Infect Immun. 2010 Feb;78(2):697-703. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00429-09. Epub 2009 Nov 23. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 19933826 Free PMC article.
-
AphA and LuxR/HapR reciprocally control quorum sensing in vibrios.Genes Dev. 2011 Feb 15;25(4):397-408. doi: 10.1101/gad.2015011. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 21325136 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of the virulence gene activator AphA from Vibrio cholerae reveals it is a novel member of the winged helix transcription factor superfamily.J Biol Chem. 2005 Apr 8;280(14):13779-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413781200. Epub 2005 Jan 12. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15647287 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of two transcriptional regulators from Bacillus cereus define the conserved structural features of a PadR subfamily.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e48015. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048015. Epub 2012 Nov 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23189126 Free PMC article.
-
Levels of the secreted Vibrio cholerae attachment factor GbpA are modulated by quorum-sensing-induced proteolysis.J Bacteriol. 2009 Nov;191(22):6911-7. doi: 10.1128/JB.00747-09. Epub 2009 Sep 4. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19734310 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carroll, P. A., K. T. Tashima, M. B. Rogers, V. J. DiRita, and S. B. Calderwood. 1997. Phase variation in tcpH modulates expression of the ToxR regulon in Vibrio cholerae. Mol. Microbiol. 25:1099-1111. - PubMed
-
- Champion, G. A., M. N. Neely, M. A. Brennan, and V. J. DiRita. 1997. A branch in the ToxR regulatory cascade of Vibrio cholerae revealed by characterization of toxT mutant strains. Mol. Microbiol. 23:323-331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

