A novel IS element, IS621, of the IS110/IS492 family transposes to a specific site in repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 12897009
- PMCID: PMC166490
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.16.4891-4900.2003
A novel IS element, IS621, of the IS110/IS492 family transposes to a specific site in repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences in Escherichia coli
Abstract
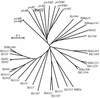
An Escherichia coli strain, ECOR28, was found to have insertions of an identical sequence (1,279 bp in length) at 10 loci in its genome. This insertion sequence (named IS621) has one large open reading frame encoding a putative protein that is 326 amino acids in length. A computer-aided homology search using the DNA sequence as the query revealed that IS621 was homologous to the piv genes, encoding pilin gene invertase (PIV). A homology search using the amino acid sequence of the putative protein encoded by IS621 as the query revealed that the protein also has partial homology to transposases encoded by the IS110/IS492 family elements, which were known to have partial homology to PIV. This indicates that IS621 belongs to the IS110/IS492 family but is most closely related to the piv genes. In fact, a phylogenetic tree constructed on the basis of amino acid sequences of PIV proteins and transposases revealed that IS621 belongs to the piv gene group, which is distinct from the IS110/IS492 family elements, which form several groups. PIV proteins and transposases encoded by the IS110/IS492 family elements, including IS621, have four acidic amino acid residues, which are conserved at positions in their N-terminal regions. These residues may constitute a tetrad D-E(or D)-D-D motif as the catalytic center. Interestingly, IS621 was inserted at specific sites within repetitive extragenic palindromic (REP) sequences at 10 loci in the ECOR28 genome. IS621 may not recognize the entire REP sequence in transposition, but it recognizes a 15-bp sequence conserved in the REP sequences around the target site. There are several elements belonging to the IS110/IS492 family that also transpose to specific sites in the repeated sequences, as does IS621. IS621 does not have terminal inverted repeats like most of the IS110/IS492 family elements. The terminal sequences of IS621 have homology with the 26-bp inverted repeat sequences of pilin gene inversion sites that are recognized and used for inversion of pilin genes by PIV. This suggests that IS621 initiates transposition through recognition of their terminal regions and cleavage at the ends by a mechanism similar to that used for PIV to promote inversion at the pilin gene inversion sites.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Bacterial repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences are DNA targets for Insertion Sequence elements.BMC Genomics. 2006 Mar 24;7:62. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-62. BMC Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16563168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conserved amino acid motifs from the novel Piv/MooV family of transposases and site-specific recombinases are required for catalysis of DNA inversion by Piv.Mol Microbiol. 2001 Feb;39(3):641-51. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02276.x. Mol Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11169105
-
Characterization of the Pseudomonas putida mobile genetic element ISPpu10: an occupant of repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences.J Bacteriol. 2006 Jan;188(1):37-44. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.1.37-44.2006. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16352819 Free PMC article.
-
Amino acid sequence homology between Piv, an essential protein in site-specific DNA inversion in Moraxella lacunata, and transposases of an unusual family of insertion elements.J Bacteriol. 1994 Jul;176(13):4160-4. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.13.4160-4164.1994. J Bacteriol. 1994. PMID: 8021196 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of DNA Transposition.Microbiol Spectr. 2015 Apr;3(2):MDNA3-0034-2014. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MDNA3-0034-2014. Microbiol Spectr. 2015. PMID: 26104718 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bridge RNAs direct programmable recombination of target and donor DNA.Nature. 2024 Jun;630(8018):984-993. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07552-4. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38926615 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences are DNA targets for Insertion Sequence elements.BMC Genomics. 2006 Mar 24;7:62. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-62. BMC Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16563168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transposition Behavior Revealed by High-Resolution Description of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Saltovirus Integration Sites.Viruses. 2018 May 7;10(5):245. doi: 10.3390/v10050245. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 29735891 Free PMC article.
-
Structural organization and functional properties of miniature DNA insertion sequences in yersiniae.J Bacteriol. 2006 Nov;188(22):7876-84. doi: 10.1128/JB.00942-06. Epub 2006 Sep 8. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16963573 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the Piv recombinase-related gene family of Neisseria gonorrhoeae.J Bacteriol. 2005 Feb;187(4):1276-86. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.4.1276-1286.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 15687191 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ariyoshi, M., D. G. Vassylyev, H. Iwasaki, H. Nakamura, H. Shinagawa, and K. Morikawa. 1994. Atomic structure of the RuvC resolvase: a Holliday junction-specific endonuclease from E. coli. Cell 78:1063-1072. - PubMed
-
- Ashby, M. K., and P. L. Bergquist. 1990. Cloning and sequence of IS1000, a putative insertion sequence from Thermus thermophilus HB8. Plasmid 24:1-11. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl (ed.). 1994. Current protocols in molecular biology, p. 2.4.1-2.4.5. Green Publishing Associates and Wiley-Interscience, New York, N.Y.
-
- Bachellier, S., E. Gilson, M. Hofnung, and C. W. Hill. 1996. Repeated sequences, p. 2012-2040. In F. C. Neidhardt, R. Curtiss III, J. L. Ingraham, E. C. C. Lin, K. B. Low, B. Magasanik, W. S. Reznikoff, M. Riley, M. Schaechter, and H. E. Umbarger (ed.), Escherichia coli and Salmonella: cellular and molecular biology, 2nd ed., vol. 2. ASM Press, Washington, D.C.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

