Structural basis for specific binding of Polycomb chromodomain to histone H3 methylated at Lys 27
- PMID: 12897052
- PMCID: PMC196225
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.269603
Structural basis for specific binding of Polycomb chromodomain to histone H3 methylated at Lys 27
Abstract
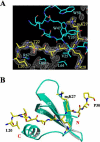
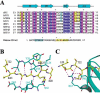
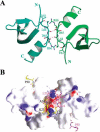
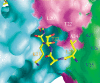
The chromodomain of Drosophila Polycomb protein is essential for maintaining the silencing state of homeotic genes during development. Recent studies suggest that Polycomb mediates the assembly of repressive higher-order chromatin structures in conjunction with the methylation of Lys 27 of histone H3 by a Polycomb group repressor complex. A similar mechanism in heterochromatin assembly is mediated by HP1, a chromodomain protein that binds to histone H3 methylated at Lys 9. To understand the molecular mechanism of the methyl-Lys 27 histone code recognition, we have determined a 1.4-A-resolution structure of the chromodomain of Polycomb in complex with a histone H3 peptide trimethylated at Lys 27. The structure reveals a conserved mode of methyl-lysine binding and identifies Polycomb-specific interactions with histone H3. The structure also reveals a dPC dimer in the crystal lattice that is mediated by residues specifically conserved in the Polycomb family of chromodomains. The dimerization of dPC can effectively account for the histone-binding specificity and provides new mechanistic insights into the function of Polycomb. We propose that self-association is functionally important for Polycomb.
Figures
References
-
- Bannister A.J., Zegerman, P., Partridge, J.F., Miska, E.A., Thomas, J.O., Allshire, R.C., and Kouzarides, T. 2001. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature 410: 120-124. - PubMed
-
- Brasher S.V., Smith, B.O., Fogh, R.H., Nietlispach, D., Thiru, A., Nielsen, P.R., Broadhurst, R.W., Ball, L.J., Murzina, N.V., and Laue, E.D. 2000. The structure of mouse HP1 suggests a unique mode of single peptide recognition by the shadow chromo domain dimer. EMBO J. 19: 1587-1597. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brunger A.T., Adams, P.D., Clore, G.M., DeLano, W.L., Gros, P., Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W., Jiang, J.S., Kuszewski, J., Nilges, M., Pannu, N.S., et al. 1998. Crystallography & NMR system: A new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D 54: 905-921. - PubMed
-
- Cao R., Wang, L., Wang, H., Xia, L., Erdjument-Bromage, H., Tempst, P., Jones, R.S., and Zhang, Y. 2002. Role of histone H3 lysine 27 methylation in Polycomb-group silencing. Science 298: 1039-1043. - PubMed
-
- Cowell I.G. and Austin, C.A. 1997. Self-association of chromo domain peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1337: 198-206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
