Molecular basis for the discrimination of repressive methyl-lysine marks in histone H3 by Polycomb and HP1 chromodomains
- PMID: 12897054
- PMCID: PMC196235
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1110503
Molecular basis for the discrimination of repressive methyl-lysine marks in histone H3 by Polycomb and HP1 chromodomains
Abstract
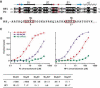
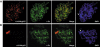
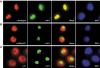
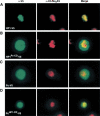
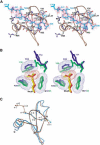
On the histone H3 tail, Lys 9 and Lys 27 are both methylation sites associated with epigenetic repression, and reside within a highly related sequence motif ARKS. Here we show that the chromodomain proteins Polycomb (Pc) and HP1 (heterochromatin protein 1) are highly discriminatory for binding to these sites in vivo and in vitro. In Drosophila S2 cells, and on polytene chromosomes, methyl-Lys 27 and Pc are both excluded from areas that are enriched in methyl-Lys 9 and HP1. Swapping of the chromodomain regions of Pc and HP1 is sufficient for switching the nuclear localization patterns of these factors, indicating a role for their chromodomains in both target site binding and discrimination. To better understand the molecular basis for the selection of methyl-lysine binding sites, we solved the 1.8 A structure of the Pc chromodomain in complex with a H3 peptide bearing trimethyl-Lys 27, and compared it with our previously determined structure of the HP1 chromodomain in complex with a H3 peptide bearing trimethyl-Lys 9. The Pc chromodomain distinguishes its methylation target on the H3 tail via an extended recognition groove that binds five additional residues preceding the ARKS motif.
Figures

References
-
- Bannister A.J., Zegerman, P., Partridge, J.F., Miska, E.A., Thomas, J.O., Allshire, R.C., and Kouzarides, T. 2001. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature 410: 120-124. - PubMed
-
- Breiling A., Turner, B.M., Bianchi, M.E., and Orlando, V. 2001. General transcription factors bind promoters repressed by Polycomb group proteins. Nature 412: 651-655. - PubMed
-
- Brunger A.T., Adams, P.D., Clore, G.M., DeLano, W.L., Gros, P., Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W., Jiang, J.S., Kuszewski, J., Nilges, M., Pannu, N.S., et al. 1998. Crystallography & NMR system: A new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Cryst. D 54: 905-921. - PubMed
-
- Cao R., Wang, L., Wang, H., Xia, L., Erdjument-Bromage, H., Tempst, P., Jones, R.S., and Zhang, Y. 2002. Role of histone H3 lysine 27 methylation in Polycomb-group silencing. Science 298: 1039-1043. - PubMed
-
- Cheutin T., McNairn, A.J., Jenuwein, T., Gilbert, D.M., Singh, P.B., and Misteli, T. 2003. Maintenance of stable heterochromatin domains by dynamic HP1 binding. Science 299: 721-725. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
