BMAL1-dependent circadian oscillation of nuclear CLOCK: posttranslational events induced by dimerization of transcriptional activators of the mammalian clock system
- PMID: 12897057
- PMCID: PMC196247
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1099503
BMAL1-dependent circadian oscillation of nuclear CLOCK: posttranslational events induced by dimerization of transcriptional activators of the mammalian clock system
Abstract
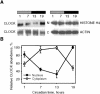
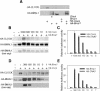
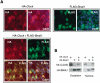
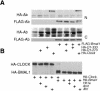
Mammalian CLOCK and BMAL1 are two members of bHLH-PAS-containing family of transcription factors that represent the positive elements of circadian autoregulatory feedback loop. In the form of a heterodimer, they drive transcription from E-box enhancer elements in the promoters of responsive genes. We have examined abundance, posttranslational modifications, cellular localization of endogenous and ectopically expressed CLOCK and BMAL1 proteins. Nuclear/cytoplasm distribution of CLOCK was found to be under circadian regulation. Analysis of subcellular localization of CLOCK in embryo fibroblasts of mice carrying different germ-line circadian mutations showed that circadian regulation of nuclear accumulation of CLOCK is BMAL1-dependent. Formation of CLOCK/BMAL1 complex following ectopic coexpression of both proteins is followed by their codependent phosphorylation, which is tightly coupled to CLOCK nuclear translocation and degradation. This binding-dependent coregulation is specific for CLOCK/BMAL1 interaction, as no other PAS domain protein that can form a complex with either CLOCK or BMAL1 was able to induce similar effects. Importantly, all posttranslational events described in our study are coupled with active transactivation complex formation, which argues for their significant functional role. Altogether, these results provide evidence for an additional level of circadian system control, which is based on regulation of transcriptional activity or/and availability of CLOCK/BMAL1 complex.
Figures



References
-
- Balsalobre A., Damiola, F., and Schibler, U. 1998. A serum shock induces circadian gene expression in mammalian tissue culture cells. Cell 93: 929-937. - PubMed
-
- Balsalobre A., Marcacci, L., and Schibler, U. 2000. Multiple signaling pathways elicit circadian gene expression in cultured Rat-1 fibroblasts. Curr. Biol. 10: 1291-1294. - PubMed
-
- Camacho F., Cilio, M., Guo, Y., Virshup, D.M., Patel, K., Khorkova, O., Styren, S., Morse, B., Yao, Z., and Keesler, G.A. 2001. Human casein kinase Iδ phosphorylation of human circadian clock proteins period 1 and 2. FEBS Lett. 489: 159-165. - PubMed
-
- Dikstein R., Ruppert, S., and Tjian, R. 1996. TAFII250 is a bipartite protein kinase that phosphorylates the base transcription factor RAP74. Cell 84: 781-790. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
