p21-Activated kinase 5 (Pak5) localizes to mitochondria and inhibits apoptosis by phosphorylating BAD
- PMID: 12897128
- PMCID: PMC166342
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.16.5526-5539.2003
p21-Activated kinase 5 (Pak5) localizes to mitochondria and inhibits apoptosis by phosphorylating BAD
Abstract
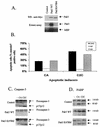
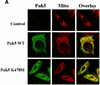
Pak5 is the most recently identified and least understood member of the p21-activated kinase (Pak) family. This kinase is known to promote neurite outgrowth in vitro, but its localization, substrates, and effects on cell survival have not been reported. We show here that Pak5 has unique properties that distinguish it from all other members of the Pak family. First, Pak5, unlike Pak1, cannot complement an STE20 mutation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Second, Pak5 binds to the GTPases Cdc42 and Rac, but these GTPases do not regulate Pak5 kinase activity, which is constitutive and stronger than any other Pak. Third, Pak5 prevents apoptosis induced by camptothecin and C2-ceramide by phosphorylating BAD on Ser-112 in a protein kinase A-independent manner and prevents the localization of BAD to mitochondria, thereby inhibiting the apoptotic cascade that leads to apoptosis. Finally, we show that Pak5 itself is constitutively localized to mitochondria, and that this localization is independent of kinase activity or Cdc42 binding. These features make Pak5 unique among the Pak family and suggest that it plays an important role in apoptosis through BAD phosphorylation.
Figures



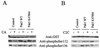






Similar articles
-
Cloning and characterization of PAK5, a novel member of mammalian p21-activated kinase-II subfamily that is predominantly expressed in brain.Oncogene. 2002 May 30;21(24):3939-48. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205478. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 12032833
-
Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of Pak5 regulates its antiapoptotic properties.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Apr;26(8):3215-30. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.8.3215-3230.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16581795 Free PMC article.
-
PAK5, a new brain-specific kinase, promotes neurite outgrowth in N1E-115 cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jan;22(2):567-77. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.2.567-577.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11756552 Free PMC article.
-
p21-Activated kinase 5: a pleiotropic kinase.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013 Dec 15;23(24):6636-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.10.051. Epub 2013 Oct 31. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013. PMID: 24215894 Review.
-
Regulation of phosphorylation pathways by p21 GTPases. The p21 Ras-related Rho subfamily and its role in phosphorylation signalling pathways.Eur J Biochem. 1996 Dec 1;242(2):171-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.0171r.x. Eur J Biochem. 1996. PMID: 8973630 Review.
Cited by
-
The overexpression of P21-activated kinase 5 (PAK5) promotes paclitaxel-chemoresistance of epithelial ovarian cancer.Mol Cell Biochem. 2013 Nov;383(1-2):191-9. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1767-7. Epub 2013 Jul 23. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23877225
-
PAK signaling in cancer.Cell Logist. 2012 Apr 1;2(2):105-116. doi: 10.4161/cl.21882. Cell Logist. 2012. PMID: 23162742 Free PMC article.
-
CDC42 binds PAK4 via an extended GTPase-effector interface.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Jan 16;115(3):531-536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1717437115. Epub 2018 Jan 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29295922 Free PMC article.
-
High expression of P21-activated kinase 5 protein is associated with poor survival in gastric cancer.Oncol Lett. 2017 Jul;14(1):404-410. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6115. Epub 2017 May 3. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28693183 Free PMC article.
-
PAK thread from amoeba to mammals.J Cell Biochem. 2009 Jul 1;107(4):579-85. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22159. J Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19350548 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bagrodia, S., and R. A. Cerione. 1999. PAK to the future. Trends Cell Biol. 9:350-355. - PubMed
-
- Bagrodia, S., S. Taylor, C. L. Creasy, J. Chernoff, and R. A. Cerione. 1995. Identification of a murine p21Cdc42/Rac activated protein kinase (PAK). J. Biol. Chem. 270:22731-22738. - PubMed
-
- Brown, J. L., L. Stowers, M. Maer, J. Trejo, S. Coughlin, and J. Chant. 1996. Human Ste20 homologue hPak1 links GTPases to the JNK MAP kinase pathway. Curr. Biol. 6:598-605. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
