Establishment and maintenance of genomic methylation patterns in mouse embryonic stem cells by Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b
- PMID: 12897133
- PMCID: PMC166327
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.16.5594-5605.2003
Establishment and maintenance of genomic methylation patterns in mouse embryonic stem cells by Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b
Abstract
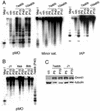
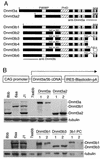
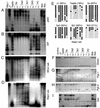
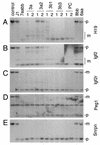
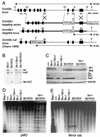
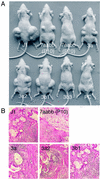
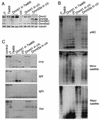
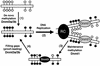
We have previously shown that the DNA methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b carry out de novo methylation of the mouse genome during early postimplantation development and of maternally imprinted genes in the oocyte. In the present study, we demonstrate that Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b are also essential for the stable inheritance, or "maintenance," of DNA methylation patterns. Inactivation of both Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b in embryonic stem (ES) cells results in progressive loss of methylation in various repeats and single-copy genes. Interestingly, introduction of the Dnmt3a, Dnmt3a2, and Dnmt3b1 isoforms back into highly demethylated mutant ES cells restores genomic methylation patterns; these isoforms appear to have both common and distinct DNA targets, but they all fail to restore the maternal methylation imprints. In contrast, overexpression of Dnmt1 and Dnmt3b3 failed to restore DNA methylation patterns due to their inability to catalyze de novo methylation in vivo. We also show that hypermethylation of genomic DNA by Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b is necessary for ES cells to form teratomas in nude mice. These results indicate that genomic methylation patterns are determined partly through differential expression of different Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b isoforms.
Figures
References
-
- Bachman, K. E., M. R. Rountree, and S. B. Baylin. 2001. Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b are transcriptional repressors that exhibit unique localization properties to heterochromatin. J. Biol. Chem. 276:32282-32287. - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu, N., S. Morin, I. C. Chute, M.-F. Robert, H. Nguyen, and A. R. MacLeod. 2002. An essential role for DNA methyltransferase DNMT3B in cancer cell survival. J. Biol. Chem. 277:28176-28181. - PubMed
-
- Bestor, T., A. Laudano, R. Mattaliano, and V. Ingram. 1988. Cloning and sequencing of a cDNA encoding DNA methyltransferase of mouse cells: the carboxyl-terminal domain of the mammalian enzymes is related to bacterial restriction methyltransferases. J. Mol. Biol. 203:971-983. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
