Pathways of DNA double-strand break repair during the mammalian cell cycle
- PMID: 12897142
- PMCID: PMC166351
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.16.5706-5715.2003
Pathways of DNA double-strand break repair during the mammalian cell cycle
Abstract
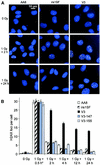
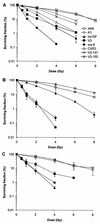
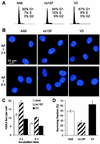
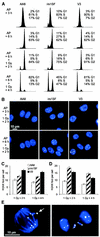
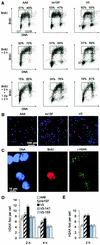
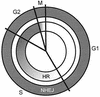
Little is known about the quantitative contributions of nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) and homologous recombination (HR) to DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair in different cell cycle phases after physiologically relevant doses of ionizing radiation. Using immunofluorescence detection of gamma-H2AX nuclear foci as a novel approach for monitoring the repair of DSBs, we show here that NHEJ-defective hamster cells (CHO mutant V3 cells) have strongly reduced repair in all cell cycle phases after 1 Gy of irradiation. In contrast, HR-defective CHO irs1SF cells have a minor repair defect in G(1), greater impairment in S, and a substantial defect in late S/G(2). Furthermore, the radiosensitivity of irs1SF cells is slight in G(1) but dramatically higher in late S/G(2), while V3 cells show high sensitivity throughout the cell cycle. These findings show that NHEJ is important in all cell cycle phases, while HR is particularly important in late S/G(2), where both pathways contribute to repair and radioresistance. In contrast to DSBs produced by ionizing radiation, DSBs produced by the replication inhibitor aphidicolin are repaired entirely by HR. irs1SF, but not V3, cells show hypersensitivity to aphidicolin treatment. These data provide the first evaluation of the cell cycle-specific contributions of NHEJ and HR to the repair of radiation-induced versus replication-associated DSBs.
Figures

References
-
- Arnaudeau, C., C. Lundin, and T. Helleday. 2001. DNA double-strand breaks associated with replication forks are predominantly repaired by homologous recombination involving an exchange mechanism in mammalian cells. J. Mol. Biol. 307:1235-1245. - PubMed
-
- Asaad, N. A., Z. C. Zeng, J. Guan, J. Thacker, and G. Iliakis. 2000. Homologous recombination as a potential target for caffeine radiosensitization in mammalian cells: reduced caffeine radiosensitization in XRCC2 and XRCC3 mutants. Oncogene 19:5788-5800. - PubMed
-
- Baumann, P., and S. C. West. 1998. Role of the human RAD51 protein in homologous recombination and double-stranded-break repair. Trends Biochem. Sci. 23:247-251. - PubMed
-
- Bezzubova, O., A. Silbergleit, Y. Yamaguchi-Iwai, S. Takeda, and J. M. Buerstedde. 1997. Reduced X-ray resistance and homologous recombination frequencies in a RAD54−/− mutant of the chicken DT40 cell line. Cell 89:185-193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
