Autophosphorylation of the catalytic subunit of the DNA-dependent protein kinase is required for efficient end processing during DNA double-strand break repair
- PMID: 12897153
- PMCID: PMC166339
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.16.5836-5848.2003
Autophosphorylation of the catalytic subunit of the DNA-dependent protein kinase is required for efficient end processing during DNA double-strand break repair
Abstract
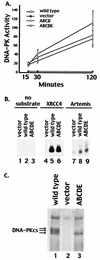
The DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) plays an essential role in nonhomologous DNA end joining (NHEJ) by initially recognizing and binding to DNA breaks. We have shown that in vitro, purified DNA-PK undergoes autophosphorylation, resulting in loss of activity and disassembly of the kinase complex. Thus, we have suggested that autophosphorylation of the DNA-PK catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) may be critical for subsequent steps in DNA repair. Recently, we defined seven autophosphorylation sites within DNA-PKcs. Six of these are tightly clustered within 38 residues of the 4,127-residue protein. Here, we show that while phosphorylation at any single site within the major cluster is not critical for DNA-PK's function in vivo, mutation of several sites abolishes the ability of DNA-PK to function in NHEJ. This is not due to general defects in DNA-PK activity, as studies of the mutant protein indicate that its kinase activity and ability to form a complex with DNA-bound Ku remain largely unchanged. However, analysis of rare coding joints and ends demonstrates that nucleolytic end processing is dramatically reduced in joints mediated by the mutant DNA-PKcs. We therefore suggest that autophosphorylation within the major cluster mediates a conformational change in the DNA-PK complex that is critical for DNA end processing. However, autophosphorylation at these sites may not be sufficient for kinase disassembly.
Figures




References
-
- Chan, D. W., and S. P. Lees-Miller. 1996. The DNA-dependent protein kinase is inactivated by autophosphorylation of the catalytic subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 271:8936-8941. - PubMed
-
- Chan, D. W., R. Ye, C. J. Veillette, and S. P. Lees-Miller. 1999. DNA-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation sites in Ku 70/80 heterodimer. Biochemistry 38:1819-1828. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
