Pex13 inactivation in the mouse disrupts peroxisome biogenesis and leads to a Zellweger syndrome phenotype
- PMID: 12897163
- PMCID: PMC166343
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.16.5947-5957.2003
Pex13 inactivation in the mouse disrupts peroxisome biogenesis and leads to a Zellweger syndrome phenotype
Abstract
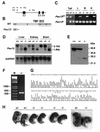
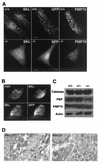
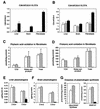
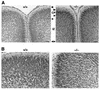
Zellweger syndrome is the archetypical peroxisome biogenesis disorder and is characterized by defective import of proteins into the peroxisome, leading to peroxisomal metabolic dysfunction and widespread tissue pathology. In humans, mutations in the PEX13 gene, which encodes a peroxisomal membrane protein necessary for peroxisomal protein import, can lead to a Zellweger phenotype. To develop mouse models for this disorder, we have generated a targeted mouse with a loxP-modified Pex13 gene to enable conditional Cre recombinase-mediated inactivation of Pex13. In the studies reported here, we crossed these mice with transgenic mice that express Cre recombinase in all cells to generate progeny with ubiquitous disruption of Pex13. The mutant pups exhibited many of the clinical features of Zellweger syndrome patients, including intrauterine growth retardation, severe hypotonia, failure to feed, and neonatal death. These animals lacked morphologically intact peroxisomes and showed deficient import of matrix proteins containing either type 1 or type 2 targeting signals. Biochemical analyses of tissue and cultured skin fibroblasts from these animals indicated severe impairment of peroxisomal fatty acid oxidation and plasmalogen synthesis. The brains of these animals showed disordered lamination in the cerebral cortex, consistent with a neuronal migration defect. Thus, Pex13(-/-) mice reproduce many of the features of Zellweger syndrome and PEX13 deficiency in humans.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional analysis of PEX13 mutation in a Zellweger syndrome spectrum patient reveals novel homooligomerization of PEX13 and its role in human peroxisome biogenesis.Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Oct 1;22(19):3844-57. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt238. Epub 2013 May 27. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23716570
-
Failure of microtubule-mediated peroxisome division and trafficking in disorders with reduced peroxisome abundance.J Cell Sci. 2006 Feb 15;119(Pt 4):636-45. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02776. Epub 2006 Jan 31. J Cell Sci. 2006. PMID: 16449325
-
A mouse model for Zellweger syndrome.Nat Genet. 1997 Sep;17(1):49-57. doi: 10.1038/ng0997-49. Nat Genet. 1997. PMID: 9288097
-
The peroxisome deficient PEX2 Zellweger mouse: pathologic and biochemical correlates of lipid dysfunction.J Mol Neurosci. 2001 Apr-Jun;16(2-3):289-97; discussion 317-21. doi: 10.1385/JMN:16:2-3:289. J Mol Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11478384 Review.
-
Zellweger syndrome knockout mouse models challenge putative peroxisomal beta-oxidation involvement in docosahexaenoic acid (22:6n-3) biosynthesis.Mol Genet Metab. 2001 Jan;72(1):1-7. doi: 10.1006/mgme.2000.3101. Mol Genet Metab. 2001. PMID: 11161822 Review.
Cited by
-
Redox interplay between mitochondria and peroxisomes.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2015 May 27;3:35. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2015.00035. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26075204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PEX13 prevents pexophagy by regulating ubiquitinated PEX5 and peroxisomal ROS.Autophagy. 2023 Jun;19(6):1781-1802. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2022.2160566. Epub 2023 Jan 1. Autophagy. 2023. PMID: 36541703 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian pexophagy at a glance.J Cell Sci. 2024 May 1;137(9):jcs259775. doi: 10.1242/jcs.259775. Epub 2024 May 16. J Cell Sci. 2024. PMID: 38752931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential Expression of Peroxisomal Proteins in Distinct Types of Parotid Gland Tumors.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 23;22(15):7872. doi: 10.3390/ijms22157872. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360635 Free PMC article.
-
The Pex1-G844D mouse: a model for mild human Zellweger spectrum disorder.Mol Genet Metab. 2014 Apr;111(4):522-532. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2014.01.008. Epub 2014 Jan 23. Mol Genet Metab. 2014. PMID: 24503136 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baes, M., P. Gressens, E. Baumgart, P. Carmeliet, M. Casteels, M. Fransen, P. Evrard, D. Fahimi, P. E. Declercq, D. Collen, P. P. van Veldhoven, and G. P. Mannaerts. 1997. A mouse model for Zellweger syndrome. Nat. Genet. 17:49-57. - PubMed
-
- Bjorkman, J., S. J. Gould, and D. I. Crane. 2002. Pex13, the mouse ortholog of the human peroxisome biogenesis disorder PEX13 gene: gene structure, tissue expression, and localization of the protein to peroxisomes. Genomics 79:162-168. - PubMed
-
- Bjorkman, J., I. Tonks, M. A. Maxwell, C. Paterson, G. F. Kay, and D. I. Crane. 2002. Conditional inactivation of the peroxisome biogenesis Pex13 gene by Cre-loxP excision. Genesis 32:179-180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
