Endocannabinoids and the regulation of body fat: the smoke is clearing
- PMID: 12897199
- PMCID: PMC166302
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI19376
Endocannabinoids and the regulation of body fat: the smoke is clearing
Abstract
Endocannabinoids, endogenous ligands of cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1), have emerged as novel and important regulators of energy homeostasis. A report in this issue demonstrates reduced body weight, fat mass, and appetite in CB1-/- mice. Examination of the underlying mechanisms reveals a dual role for endocannabinoids as they affect both appetite and peripheral lipolysis.
Figures
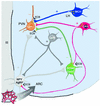
Comment on
-
The endogenous cannabinoid system affects energy balance via central orexigenic drive and peripheral lipogenesis.J Clin Invest. 2003 Aug;112(3):423-31. doi: 10.1172/JCI17725. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 12897210 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K, Thun MJ. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:1625–1638. - PubMed
-
- Eckel RH. Obesity and heart disease: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Nutrition Committee, American Heart Association. Circulation. 1997;96:3248–3250. - PubMed
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Johnson CL. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999-2000. JAMA. 2002;288:1723–1727. - PubMed
-
- Matsuda LA, Lolait SJ, Brownstein MJ, Young AC, Bonner TI. Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression pf the cloned cDNA. Nature. 1990;346:561–564. - PubMed
-
- Munro S, Thomas KL, Abu-Shaar M. Molecular characterization of a peripheral receptor for cannabinoids. Nature. 1993;365:61–65. - PubMed

