NSAIDs and enantiomers of flurbiprofen target gamma-secretase and lower Abeta 42 in vivo
- PMID: 12897211
- PMCID: PMC166298
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI18162
NSAIDs and enantiomers of flurbiprofen target gamma-secretase and lower Abeta 42 in vivo
Abstract
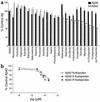
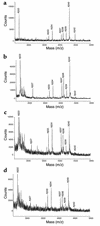
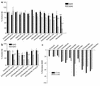
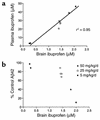
Epidemiologic studies demonstrate that long-term use of NSAIDs is associated with a reduced risk for the development of Alzheimer disease (AD). In this study, 20 commonly used NSAIDs, dapsone, and enantiomers of flurbiprofen were analyzed for their ability to lower the level of the 42-amino-acid form of amyloid beta protein (Abeta42) in a human H4 cell line. Thirteen of the NSAIDs and the enantiomers of flurbiprofen were then tested in acute dosing studies in amyloid beta protein precursor (APP) transgenic mice, and plasma and brain levels of Abeta and the drug were evaluated. These studies show that (a). eight FDA-approved NSAIDs lower Abeta42 in vivo, (b). the ability of an NSAID to lower Abeta42 levels in cell culture is highly predicative of its in vivo activity, (c). in vivo Abeta42 lowering in mice occurs at drug levels achievable in humans, and (d). there is a significant correlation between Abeta42 lowering and levels of ibuprofen. Importantly, flurbiprofen and its enantiomers selectively lower Abeta42 levels in broken cell gamma-secretase assays, indicating that these compounds directly target the gamma-secretase complex that generates Abeta from APP. Of the compounds tested, meclofenamic acid, racemic flurbiprofen, and the purified R and S enantiomers of flurbiprofen lowered Abeta42 levels to the greatest extent. Because R-flurbiprofen reduces Abeta42 levels by targeting gamma-secretase and has reduced side effects related to inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX), it is an excellent candidate for clinical testing as an Abeta42 lowering agent.
Figures
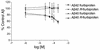
Comment in
-
Amyloid beta and Alzheimer disease therapeutics: the devil may be in the details.J Clin Invest. 2003 Aug;112(3):321-3. doi: 10.1172/JCI19420. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 12897198 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer’s disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol. Rev. 2001;81:741–766. - PubMed
-
- Hardy JA, Higgins GA. Alzheimer’s disease: the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science. 1992;256:184–185. - PubMed
-
- Golde TE, Eckman CB, Younkin SG. Biochemical detection of Aβ isoforms: implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. . Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2000; 1502:172–187. - PubMed
-
- Younkin SG. The role of A beta 42 in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Physiol. (Paris). 1998;92:289–292. - PubMed
-
- Scheuner D, et al. Secreted amyloid beta-protein similar to that in the senile plaques of Alzheimer’s disease is increased in vivo by the presenilin 1 and 2 and APP mutations linked to familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 1996;2:864–870. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

