The interaction of two homeobox genes, BREVIPEDICELLUS and PENNYWISE, regulates internode patterning in the Arabidopsis inflorescence
- PMID: 12897247
- PMCID: PMC167164
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.012856
The interaction of two homeobox genes, BREVIPEDICELLUS and PENNYWISE, regulates internode patterning in the Arabidopsis inflorescence
Abstract
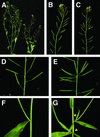
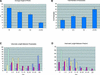
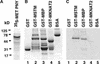
Plant architecture results from the activity of the shoot apical meristem, which initiates leaves, internodes, and axillary meristems. KNOTTED1-like homeobox (KNOX) genes are expressed in specific patterns in the shoot apical meristem and play important roles in plant architecture. KNOX proteins interact with BEL1-like (BELL) homeodomain proteins and together bind a target sequence with high affinity. We have obtained a mutation in one of the Arabidopsis BELL genes, PENNYWISE (PNY), that appears phenotypically similar to the KNOX mutant brevipedicellus (bp). Both bp and pny have randomly shorter internodes and display a slight increase in the number of axillary branches. The double mutant shows a synergistic phenotype of extremely short internodes interspersed with long internodes and increased branching. PNY is expressed in inflorescence and floral meristems and overlaps with BP in a discrete domain of the inflorescence meristem where we propose the internode is patterned. The physical association of the PNY and BP proteins suggests that they participate in a complex that regulates early patterning events in the inflorescence meristem.
Figures





References
-
- Cline, M.G. (1994). The role of hormones in apical dominance: New approaches to an old problem in plant development. Physiol. Plant. 90, 230–237.
-
- Cutter, E.G. (1971). Plant Anatomy: Experiment and Interpretation. (London: Edward Arnold).
-
- Digby, J., and Wareing, P.F. (1966). The effect of applied growth hormones on cambial activity and the differentiation of the cambial derivatives. Ann. Bot. 30, 539–548.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

