Control of cellulose synthase complex localization in developing xylem
- PMID: 12897249
- PMCID: PMC167166
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.012815
Control of cellulose synthase complex localization in developing xylem
Abstract
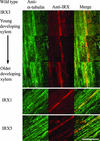
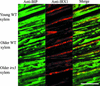
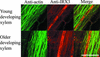
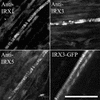
Cellulose synthesis in the developing xylem vessels of Arabidopsis requires three members of the cellulose synthase (CesA) gene family. In young vessels, these three proteins localize within the cell, whereas in older vessels, all three CesA proteins colocalize with bands of cortical microtubules that mark the sites of secondary cell wall deposition. In the absence of one subunit, however, the remaining two subunits are retained in the cell, demonstrating that all three CesA proteins are required to assemble a functional complex. CesA proteins with altered catalytic activity localize normally, suggesting that cellulose synthase activity is not required for this localization. Cortical microtubule arrays are required continually to maintain normal CesA protein localization. By contrast, actin microfilaments do not colocalize with the CesA proteins and are unlikely to play a direct role in their localization. Green fluorescent protein-tagged CesA reveals a novel process in which the structure and/or local environment of the cellulose synthase complex is altered rapidly.
Figures




References
-
- Anthony, R.G., Waldin, T.R., Ray, J.A., Bright, S.W.J., and Hussey, P.J. (1998). Herbicide resistance caused by spontaneous mutation of the cytoskeletal protein tubulin. Nature 393, 260–263. - PubMed
-
- Arioli, T., et al. (1998). Molecular analysis of cellulose biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Science 279, 717–720. - PubMed
-
- Baskin, T.I. (2001). On the alignment of cellulose microfibrils by cortical microtubules: A review and a model. Protoplasma 215, 150–171. - PubMed
-
- Brower, D.L., and Hepler, P.K. (1976). Microtubules and secondary wall deposition in xylem: The effects of isopropyl N-phenylcarbamate. Protoplasma 87, 91–111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

