The Arabidopsis basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family
- PMID: 12897250
- PMCID: PMC167167
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.013839
The Arabidopsis basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family
Abstract
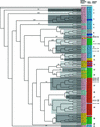
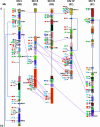
The basic/helix-loop-helix (bHLH) proteins are a superfamily of transcription factors that bind as dimers to specific DNA target sites and that have been well characterized in nonplant eukaryotes as important regulatory components in diverse biological processes. Based on evidence that the bHLH protein PIF3 is a direct phytochrome reaction partner in the photoreceptor's signaling network, we have undertaken a comprehensive computational analysis of the Arabidopsis genome sequence databases to define the scope and features of the bHLH family. Using a set of criteria derived from a previously defined consensus motif, we identified 147 bHLH protein-encoding genes, making this one of the largest transcription factor families in Arabidopsis. Phylogenetic analysis of the bHLH domain sequences permits classification of these genes into 21 subfamilies. The evolutionary and potential functional relationships implied by this analysis are supported by other criteria, including the chromosomal distribution of these genes relative to duplicated genome segments, the conservation of variant exon/intron structural patterns, and the predicted DNA binding activities within subfamilies. Considerable diversity in DNA binding site specificity among family members is predicted, and marked divergence in protein sequence outside of the conserved bHLH domain is observed. Together with the established propensity of bHLH factors to engage in varying degrees of homodimerization and heterodimerization, these observations suggest that the Arabidopsis bHLH proteins have the potential to participate in an extensive set of combinatorial interactions, endowing them with the capacity to be involved in the regulation of a multiplicity of transcriptional programs. We provide evidence from yeast two-hybrid and in vitro binding assays that two related phytochrome-interacting members in the Arabidopsis family, PIF3 and PIF4, can form both homodimers and heterodimers and that all three dimeric configurations can bind specifically to the G-box DNA sequence motif CACGTG. These data are consistent, in principle, with the operation of this combinatorial mechanism in Arabidopsis.
Figures




Comment in
-
Update on the basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Cell. 2003 Nov;15(11):2497-502. doi: 10.1105/tpc.151140. Plant Cell. 2003. PMID: 14600211 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Atchley, W.R., Therhalle, W., and Dress, A. (1999). Positional dependence, cliques and predictive motifs in the bHLH protein domain. J. Mol. Evol. 48, 501–516. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

